Roman sports went beyond just the famous gladiator games. They included a wide variety of athletic events and competitions that were an important part of social life in ancient Rome. These activities served many purposes, such as entertainment and political influence.
Understanding these aspects helps us see how sports shaped not only individual lives but also the larger Roman society. The impact of these competitions can still be seen in modern sports culture today.
For those interested in exploring more about Ancient Rome, including its sports, legal systems influenced by laws like the Twelve Tables, significant historical figures such as Scipio Africanus, or the complex story of its rise and fall, there are many resources available that bring this rich history to life. Additionally, understanding the role of the Roman Army in shaping the empire can provide further insights into this fascinating period.
Chariot Racing: The Pinnacle of Roman Sport
Chariot racing was the most exciting and popular sport in ancient Rome. Races took place in large arenas called circuses, with the Circus Maximus being the most famous one. This grand structure could hold up to 250,000 spectators, making it a central hub for public entertainment and social interaction. To understand the importance of such events in ancient Roman society, we can explore the spectacle of ancient Rome, which included not only chariot races but also gladiatorial contests and theatrical performances.
1. Description of Chariot Racing
Competitors raced in lightweight chariots pulled by teams of horses, typically four to a chariot. Races consisted of seven laps around a track, emphasizing speed and skill. The atmosphere was electrifying, with fans cheering passionately for their favorite factions.
2. Architecture and Significance of Circus Maximus
The Circus Maximus featured tiered seating, allowing thousands to witness the high-stakes races up close. Its design reflected Roman engineering prowess and served as a symbol of power and community engagement.
3. Rivalries Between Factions
Fans divided themselves into factions identified by colors—most notably the Blue and Green teams. These rivalries transcended mere competition; they fostered social identities among supporters and could even incite political unrest or violence.
4. Dangers and Excitement
Chariot racing was fraught with peril. Crashes were common, often leading to serious injuries or fatalities among both charioteers and horses. The thrill of watching these dangerous races captivated audiences, fueling their fervor for this dramatic spectacle.
Chariot racing encapsulated the essence of Roman sports culture—intense competition, communal pride, and thrilling entertainment. This aspect of Roman culture has left an indelible mark on history, contributing significantly to the legacy of ancient Rome which continues to shape Western civilization today.

Hand-to-Hand Combat Sports: Boxing and Wrestling
Boxing in ancient Rome emerged as a prominent sport, evolving from Greek traditions. The Romans adapted boxing techniques, emphasizing not only strength but also strategy.
Rules and Tactics
- Matches took place in an enclosed area, often within a palaestra (wrestling school).
- Fighters wore gloves made of leather or sometimes even metal, leading to brutal confrontations.
- Techniques included various strikes aimed at incapacitating the opponent, with strategies revolving around quick footwork and defensive maneuvers.
Palaestrae
- These training schools were crucial for aspiring boxers.
- Palaestrae served as social hubs, where physical training coincided with discussions on philosophy and politics.
- They provided structured environments for learning combat skills and fostering camaraderie among athletes.
Wrestling enjoyed immense popularity, particularly among Roman youth.
Campus Martius
- This central area was a vibrant hub for athletic activities.
- Young wrestlers practiced various holds and techniques, competing in friendly matches that enhanced their skills and camaraderie.
- The practices emphasized both physical prowess and character development, making wrestling an essential rite of passage for many young men.
Both boxing and wrestling not only showcased individual skill but also reflected broader societal values of strength, discipline, and community engagement within Roman culture. These sports were integral to the social fabric of ancient Rome, which also included other aspects such as the engineering prowess evident in Roman roads that connected far-flung regions of the empire or the incredible engineering feats that have left a lasting impact on contemporary infrastructure systems. Moreover, the cultural significance of sports is akin to that of gladiators, who were admired for their skills yet also victims of a complex social system. Such dynamics are part of the larger tapestry of [art and culture in ancient Rome](https://www.menofpompeii.com/art-and-culture-in-ancient-rome-a-journey-through-sculpture-and-mosaics), which reflects the ingenuity and creativity of this ancient civilization. Lastly, the social hierarchy during this period is exemplified by the patricians, who were the wealthy elite distinct from the working-class plebeians, influencing not just politics but also lifestyle choices within Roman society.

Lesser-Known Sports: Harpastum and Beyond
Harpastum was an engaging team sport that captured the spirit of competition in ancient Rome. This game, resembling modern rugby, involved two teams competing to retain possession of a small ball while attempting to score by crossing a designated line.
Key features of Harpastum include:
- Gameplay: The objective was to keep the ball away from the opposing team, utilizing both strategy and physical strength. Players often employed aggressive tactics, making it a contact-heavy sport.
- Field: Matches were typically played on an open area, allowing for dynamic movement and engagement among players. The rules were flexible, leading to varied styles of play depending on regional preferences.
- Cultural Significance: Harpastum was not as widely documented as other sports but held cultural relevance. It provided opportunities for social interaction among different classes, promoting teamwork and camaraderie.
Although lesser-known compared to chariot racing or boxing, Harpastum reflects the diversity of Roman sports beyond gladiators. Its presence in the athletic culture illustrates how Romans valued competition in various forms.

Public Games and Festivals: A Community Affair
Public games and festivals were an important part of Roman society. These events were more than just sports competitions; they were grand shows that involved the entire population and reinforced social structures.
Political Tool
Emperors and politicians often sponsored public games to gain favor among the citizens. By providing entertainment, they could distract from political issues or unrest. Generous games showcased wealth and power, creating a bond between the rulers and the ruled. This tactic was part of a larger political strategy that evolved during the transition from monarchy to a republican system, which marked a significant shift in governance around 509 BCE. The resulting complex political structure laid the foundation for modern democracies.
Diverse Activities
The public games included a variety of attractions such as:
- Athletic competitions: From chariot races to wrestling matches, these events drew massive crowds.
- Theatrical performances: Plays and dramas were staged, enriching the cultural landscape.
- Beast hunts: Exotic animals were showcased, illustrating Rome’s expansive reach.
- Naval battles: Ingeniously flooded arenas hosted dramatic mock battles on water.
Social Cohesion
These gatherings fostered a sense of community among participants and spectators alike. Citizens from different social classes came together to celebrate, root for their favorite athletes or factions, and share in the excitement of competition. This collective experience helped to unify a diverse population under the banner of Roman identity.
Public games were more than just sports; they represented the values of Roman culture—competition, public engagement, and loyalty to leadership. By combining entertainment with political strategy, these festivals became an essential part of life in ancient Rome.
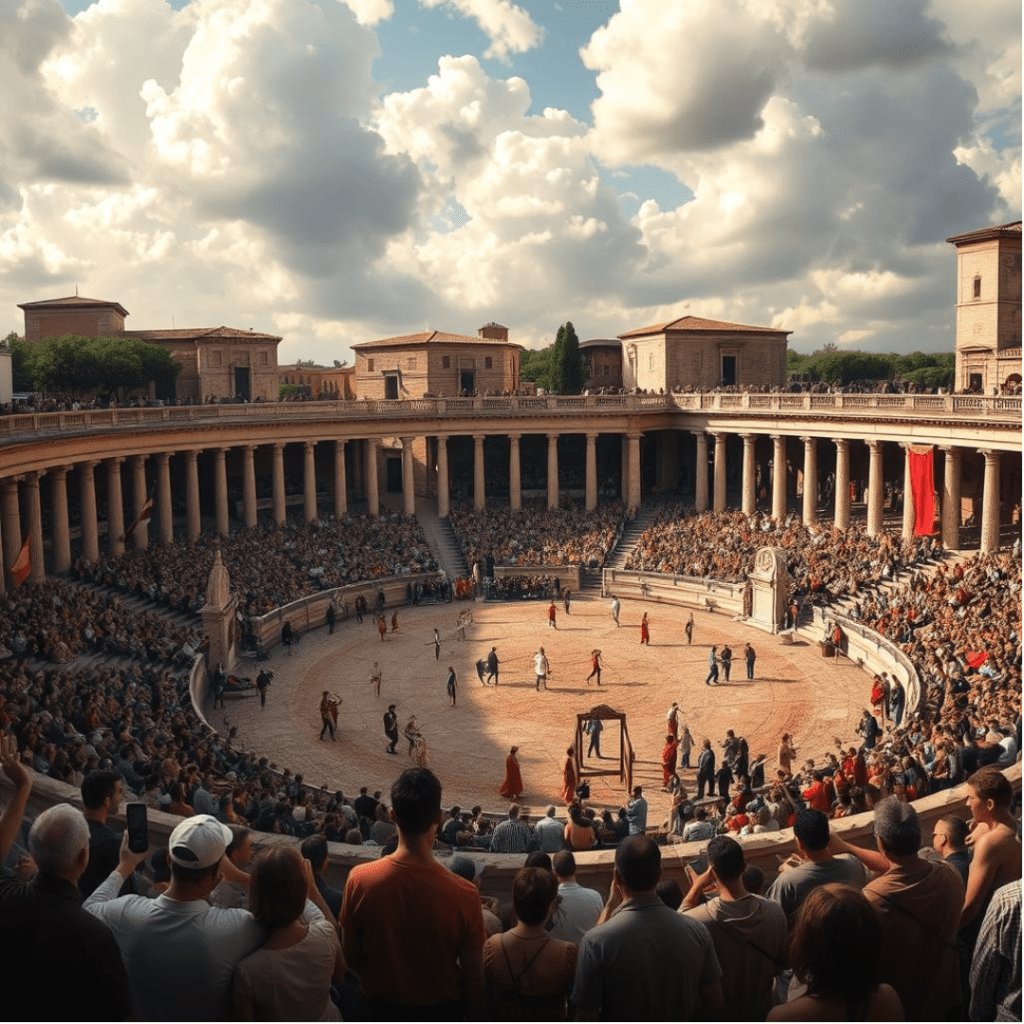
Leisure Activities Beyond Competitive Sports: Swimming, Horseback Riding, Board Games, and Social Engagement
Leisure activities in ancient Rome played a significant role in daily life, providing a welcome escape from the rigors of work and competition. Key activities included:
- Swimming: Romans enjoyed swimming in rivers, lakes, and constructed pools. This activity was not merely for pleasure; it served as a crucial method for maintaining fitness and refreshing oneself in the warm climate.
- Horseback Riding: This pastime had dual importance. While it offered leisure to the upper classes, it also served as essential training for military readiness. Roman cavalry units relied on skilled riders, making this activity both a sport and a duty.
- Board Games: Popular games such as dice and knucklebones captivated many Romans. These games provided entertainment and fostered social connections among participants.
The communal aspect of these leisure pursuits strengthened bonds within families and friends. Engaging in games often facilitated conversations on various topics ranging from politics to philosophy. Such interactions reflected the cultural emphasis on both physical prowess and intellectual engagement, showcasing the multifaceted nature of Roman society beyond competitive athletics.
In addition to these traditional leisure activities, modern interpretations have emerged that allow individuals to explore historical contexts in unique ways. For instance, role-playing games like Second Life enable players to immerse themselves in virtual worlds that replicate ancient Roman settings. This blend of leisure and education offers a fascinating insight into the past.
It’s also important to note that leisure activities were influenced by the social class divide prevalent during ancient Rome. The patricians enjoyed more luxurious leisure pursuits compared to the plebeians, who formed the majority of the population and led simpler lives. Understanding plebeian life is essential for grasping the social dynamics of Rome.
Moreover, these leisure activities were not just about relaxation but also served other purposes. For example, horseback riding was not only a form of recreation but also essential training for military readiness, highlighting how intertwined leisure and duty were in Roman society.
Lastly, it’s worth mentioning that religion played a significant role in shaping these leisure activities. The religious practices of the Romans were not merely a set of beliefs but a comprehensive system that intertwined with every aspect of their lives, influencing politics, culture, and social structures.
Training Regimens and Facilities for Athletes
In ancient Rome, athletes honed their skills in specialized training facilities known as gymnasia and palaestrae. These venues served as essential hubs for physical preparation and athletic education.
1. Gymnasia
These were larger complexes that combined exercise with other activities. Typically equipped with open-air spaces, walking paths, and sometimes even libraries, gymnasia encouraged a holistic approach to fitness. Athletes trained not only their bodies but also engaged in intellectual discussions.
2. Palaestrae
Focused primarily on combat sports like boxing and wrestling, palaestrae provided a more intimate setting for training. Equipped with sand-covered floors, they facilitated the practice of various techniques. These schools were crucial for developing the skills needed for competition.
Training regimens in these facilities were rigorous and structured. Athletes followed specific routines designed to enhance strength, agility, and endurance. Coaches emphasized discipline and dedication, instilling a sense of responsibility in their students.
Social interaction flourished within these spaces. Athletes often formed close bonds, sharing techniques and strategies while competing against one another. This camaraderie contributed to the vibrant athletic culture of ancient Rome.
The significance of these training facilities cannot be overstated; they laid the groundwork for the athletic prowess displayed in public games and competitions across the empire.
Gender Dynamics in Roman Sports
The world of Roman sports was mainly shaped by men. Male athletes were highly visible and celebrated in society for their physical abilities. Here are some key aspects of this dynamic:
1. Limited Opportunities for Women
Women faced significant obstacles when it came to competitive sports. Their participation was limited, primarily due to societal norms that prioritized traditional gender roles. This issue was further complicated by the legal status of Roman women, which had a mix of rights and restrictions that greatly impacted gender dynamics in ancient Rome.
2. Female Athletes
Despite these limitations, some women did pursue athletic activities. Notable examples include noblewomen who took part in events like horse racing or swimming but only in private settings.
3. Societal Views on Female Athletes
The prevailing attitudes towards female athletes often saw them as exceptions rather than the norm. Women’s athleticism was frequently viewed with doubt or mockery, reflecting the broader societal views influenced by Stoicism, a philosophy that shaped the thoughts and actions of important thinkers throughout the empire.
4. Comparison with Other Cultures
Unlike Greek practices where women’s sports received more recognition, Roman culture mostly ignored female athletes in public competitions.
5. Impact on Future Generations
These dynamics contributed to a long-standing belief that athletics were primarily for men, shaping societal views on gender roles that continued into later periods.
Gender roles not only affected how many women participated in sports but also influenced the cultural importance given to different sports in Roman society.
Conclusion
The legacy of Roman sports extends far beyond gladiatorial contests, showcasing a rich tapestry of athletic endeavors that reflect cultural values. Ancient competitions not only provided entertainment but also fostered community engagement and political favor.
Key influences include:
- Chariot Racing: The intense rivalries formed in this sport resonate with modern competitive environments.
- Combat Sports: Boxing and wrestling laid the groundwork for contemporary martial arts.
- Leisure Activities: Social games highlight the importance of camaraderie in sports.
These historical practices continue to shape modern sports culture, emphasizing competition, teamwork, and the spirit of community. Understanding the significance of Roman athletics allows you to appreciate their role in developing today’s sports landscape. Engaging with these ancient traditions enriches your perspective on how sports serve as a cultural reflection across time.
Moreover, the impact of Roman culture extends beyond sports, influencing various aspects of our society today. For instance, Roman Law, which originated around 753 BCE and lasted until the 5th century CE, has played a crucial role in shaping modern legal systems. Its principles are still relevant in various legal systems today, marking it as a significant achievement in the history of law. This is further exemplified by the Corpus Juris Civilis, a comprehensive codification commissioned by Emperor Justinian I in the 6th century AD that preserved ancient Roman legal principles while adapting them to contemporary society’s needs.
Additionally, the influence of Roman mythology on modern culture cannot be overlooked. The Romans inherited much from the Greeks and adapted these myths to reflect their societal norms and political aspirations, leaving a lasting impact on our cultural landscape.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What were some popular sports in ancient Rome besides gladiator fights?
In addition to gladiatorial combat, ancient Rome featured a variety of sports including chariot racing, boxing, wrestling, and lesser-known games like Harpastum. These activities played a significant role in Roman culture and society.
Why was chariot racing considered the pinnacle of Roman sport?
Chariot racing was immensely popular in ancient Rome, particularly at the Circus Maximus. The excitement of the races, along with fierce rivalries between factions such as the Blues and Greens, made it a thrilling spectacle that captivated audiences and influenced social dynamics.
What were the training facilities like for Roman athletes?
Roman athletes trained in specialized facilities known as gymnasia and palaestrae. These venues provided spaces for various athletic pursuits, including boxing and wrestling, allowing athletes to hone their skills and prepare for competitions.
How did public games and festivals function in Roman society?
Public games and festivals served as vital community events in ancient Rome, often organized to gain political favor. They showcased athletic prowess and fostered a sense of unity among citizens while celebrating cultural traditions.
What leisure activities did Romans engage in beyond competitive sports?
Romans enjoyed various leisure activities such as swimming in rivers and pools, horseback riding for both enjoyment and military training, and playing board games like dice and knucklebones. These pastimes reflected social engagement within Roman culture.
What was the role of gender dynamics in Roman sports?
Roman athletics were predominantly male-dominated, with limited opportunities for female participation. This gender dynamic highlighted societal norms of the time but also laid the groundwork for future discussions on gender roles within sports.

