The Roman Empire is renowned for its remarkable network of roads, which were instrumental in maintaining its vast territorial expanse. These roads, stretching over 400,000 kilometers, exemplify the ingenuity and strategic foresight of Roman engineering.
This article delves into the pivotal role Roman roads played in military expansion. It will explore how these roads enabled rapid troop movements, ensured efficient communication, and supported supply lines. Furthermore, the dual purpose of roads in fostering both military logistics and economic growth will be examined.
By offering a comprehensive analysis, the article seeks to illuminate the multifaceted impact of Roman road infrastructure on the empire’s military successes and its enduring legacy. This exploration will underscore the roads’ historical significance, providing insights into their contribution to Rome’s dominance.
Strategic Importance of Roman Roads
Facilitating Rapid Troop Movement
The Roman road network was meticulously engineered to facilitate the swift movement of military forces across the vast expanse of the empire. Built with durable materials and characterized by straight alignments, these roads enabled troops to travel faster than ever before. Such strategic mobility provided the Roman military with a significant tactical advantage, allowing for surprise attacks and rapid responses to enemy actions. This capability was crucial in maintaining Roman dominance and effectively projecting power across conquered territories.
Enhancing Communication and Supply Lines
The roads also played a pivotal role in enhancing communication and supply logistics. They connected military bases, cities, and supply depots, ensuring efficient transport of supplies, reinforcements, and information. The construction of way stations and rest stops further improved logistical efficiency by supporting travelers and merchants. This network was indispensable for maintaining control over vast territories, as it facilitated the rapid transmission of orders and the movement of resources essential for trade and governance.
Via Appia: The Backbone of Roman Expansion
Constructed in 312 BC, the Via Appia, often hailed as the ‘Queen of Roads,’ was pivotal in the expansion of the Roman Empire. This ancient marvel was among the earliest Roman roads, designed to connect Rome with the southern provinces of Italy. Its strategic significance lay in facilitating military, trade, and communication links between Rome and its provinces, thus bolstering Roman control and influence.

The Via Appia played a dual role in military and economic contexts. Militarily, it enabled the rapid movement of legions and supplies, crucial for maintaining control over vast territories and responding swiftly to threats. For instance, it provided a direct route for troop deployments, enhancing Rome’s military readiness and efficiency.
Economically, the Via Appia was a vital trade artery. It connected Rome to ports and resource-rich regions, facilitating the movement of goods such as grain, wine, and olive oil. This trade route not only contributed to the economic prosperity of the Roman Empire but also supported cultural exchange, spreading ideas and customs across the provinces. The Via Appia’s enduring legacy set a precedent for future infrastructure development throughout the empire.
Key Roads and Their Roles
The Roman Empire’s vast network of roads was indispensable for military logistics, enabling the rapid movement of troops and supplies. Several key roads played pivotal roles in various military campaigns and the administration of the empire.
- Via Appia: Often referred to as the ‘Queen of Roads’, it connected Rome to Brindisi, facilitating quick troop movements and supply transport to the southern regions.
- Via Augusta: This road linked the northern provinces to Rome, enhancing military access to the Alps and supporting the movement of legions.
- Via Egnatia: Spanning from the Adriatic Sea to Byzantium, it was crucial for military operations in the eastern provinces and ensured swift troop deployments.
- Via Claudia Augusta: Connecting the Po River to the Adriatic Sea, it provided a vital route for transporting troops and resources across northern Italy.
- Via Aurelia: Running along the western coast, this road offered access to key military ports and facilitated campaigns in coastal regions.
- Via Flaminia: Linking Rome to the Adriatic Sea, it served military expeditions into northern Italy.
The strategic design and maintenance of these roads ensured efficient logistics, allowing the Roman military to exert control over conquered territories and maintain a robust supply chain.
Economic Growth Through Trade Routes
The Roman Empire’s extensive road networks were instrumental in facilitating trade, significantly impacting the economic prosperity of the empire. Spanning over 250,000 miles, these roads connected diverse regions, enabling the efficient movement of goods and people. Products such as olive oil, wine, and grain could be transported across vast distances, enhancing trade between provinces and urban centers.

This infrastructure fostered economic integration, allowing local economies to exchange goods and resources, leading to a more interconnected empire. Historical records indicate that the trade volume increased as merchants capitalized on the roads’ connectivity, effectively transforming the Roman economy. Towns and cities developed along these routes, becoming bustling hubs of commerce and trade.
Moreover, the roads played a dual role by supporting military logistics, which in turn safeguarded trade routes. The protection of these routes was crucial for maintaining economic stability and growth. This synergy between military and economic strategies exemplifies the foresight of Roman infrastructure planning, which laid the foundation for sustained economic expansion and urbanization throughout the empire.
Military Campaigns and Road Utilization
The Roman Empire’s military prowess was significantly enhanced by its extensive network of roads, which played a pivotal role in several key campaigns. While specific examples are scarce, historical analyses suggest that the roads were integral during the Second Punic War, where the rapid deployment of troops was crucial in countering Hannibal’s advances. Notably, the expression “all roads lead to Rome” underscores the strategic planning involved in Rome’s military expeditions.

Another major campaign that benefited from the road system was the conquest of Gaul. Julius Caesar’s forces utilized these routes for effective logistical support, enabling swift movement and communication, which were vital in maintaining momentum and control over the newly conquered territories. As the historian Tacitus noted, “The roads were the veins and arteries of the empire,” highlighting their importance in military operations.
The strategic advantages gained from these roads included rapid troop movement, logistical efficiency, and improved communication. These factors not only facilitated military expansion but also ensured the stability and sustainability of Roman control across vast regions. The roads thus served as both a tool of conquest and a symbol of Roman engineering prowess, bolstering the empire’s military and administrative capabilities.
Construction Techniques of Roman Roads
The construction of Roman roads was a marvel of engineering that significantly contributed to their durability and longevity. Roman engineers employed a range of advanced techniques to create a network that facilitated military and economic expansion. A crucial aspect of their design was meticulous surveying and planning, using tools like the groma to ensure straight paths and minimal obstacles.
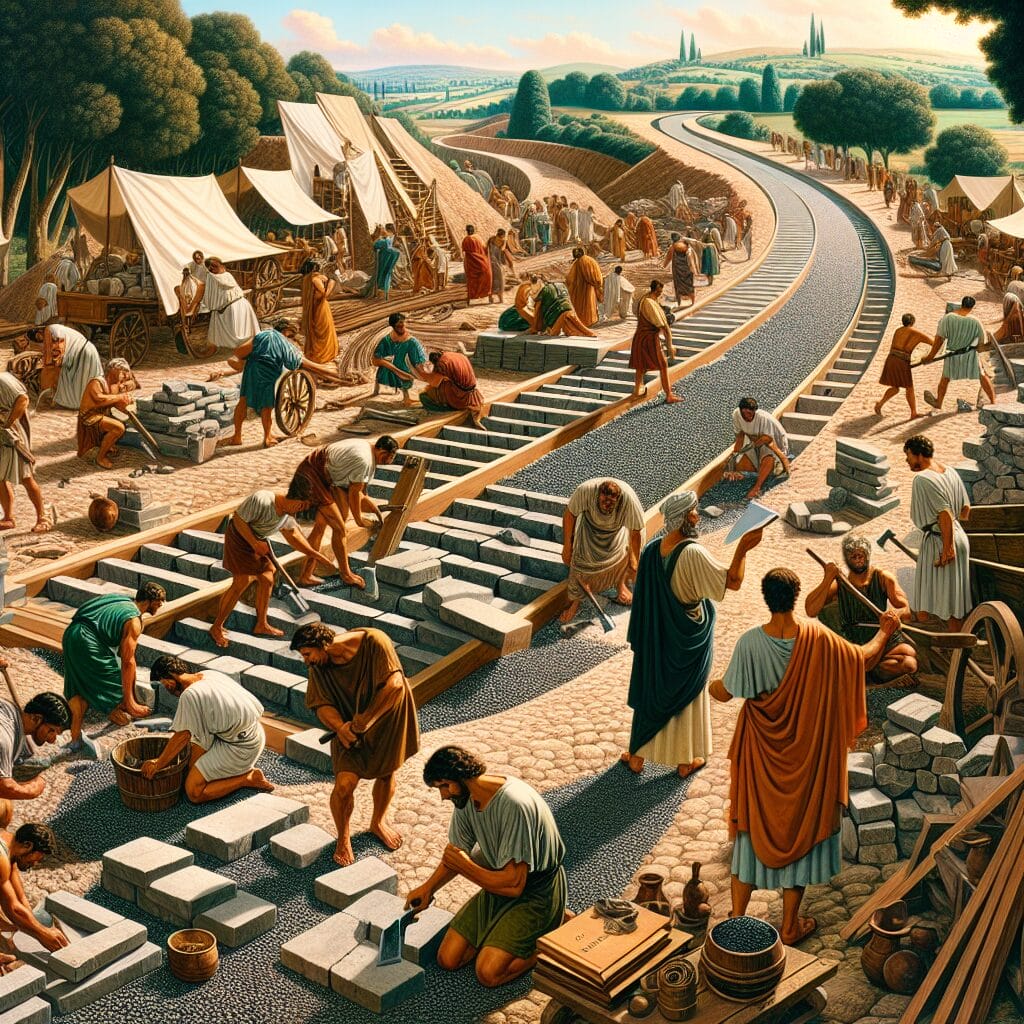

The roads featured a layered construction technique, beginning with a foundation of large stones. This was followed by smaller stones, gravel, and a surface layer of tightly packed stones or paving slabs. This multi-layer approach not only distributed weight effectively but also facilitated drainage, preventing erosion.
To enhance durability, the Romans made use of local materials, such as basalt and concrete, a revolutionary material that included pozzolana, which added resilience to weathering. Additionally, the roads were constructed with a slight camber and drainage system, allowing water to run off efficiently, further protecting the infrastructure.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Layered Construction | Foundation of large stones, followed by gravel and paving slabs |
| Camber and Drainage | Slight convex shape for water runoff |
| Materials | Use of local stone and concrete |
These innovations, combined with a systematic maintenance regime, resulted in roads that have endured for centuries. The Roman emphasis on standardization and planning ensured that these roads served both military and trade purposes, underpinning the empire’s vast reach and influence.
Maintenance of Roman Roads
The maintenance of Roman roads was a pivotal aspect of their enduring functionality and played a crucial role in sustaining military efficiency. The Roman Empire implemented a systematic approach to upkeep, ensuring that roads remained in optimal condition for both military and trade purposes. Regular maintenance was vital to prevent deterioration and extend the lifespan of these strategic infrastructures.
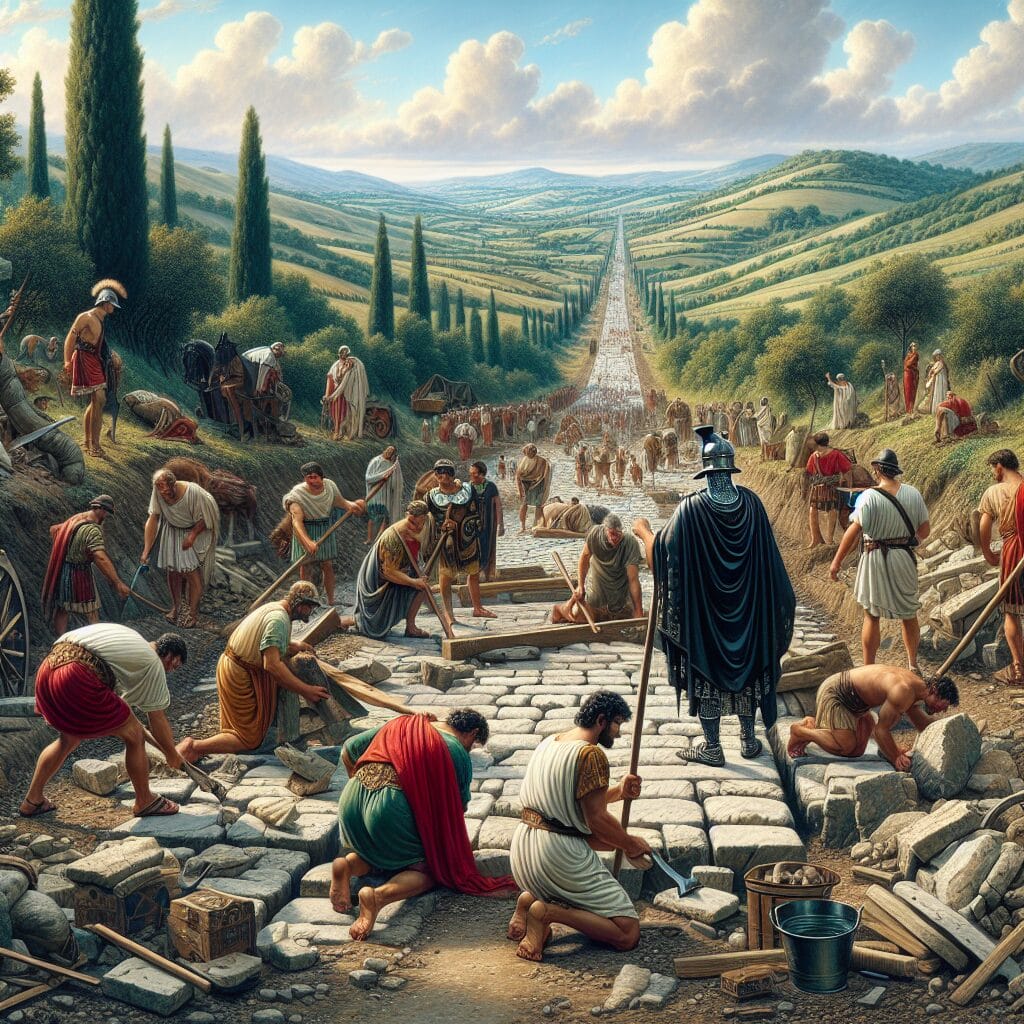

An established network of maintenance crews was tasked with inspecting and repairing roads. These crews were responsible for addressing wear and tear caused by heavy use and environmental factors. Documented repairs often involved replacing damaged paving stones, clearing drainage ditches to prevent water accumulation, and reinforcing the road’s structure with additional materials when necessary.
The proactive maintenance strategy of Roman roads not only facilitated the rapid movement of troops but also ensured reliable supply lines. This system of upkeep was instrumental in maintaining the Roman Empire’s expansive reach, allowing for quick mobilization and strategic military planning. The commitment to regular maintenance highlights the Romans’ understanding of infrastructure as a vital component of their military and economic strength.
Influence on Roman Military Strategy
The strategic planning of Roman roads was instrumental in shaping the military strategy of the Roman Empire. The meticulously planned network of roads allowed for the rapid deployment and efficient movement of Roman legions across vast territories. This infrastructure enabled the empire to project its military power effectively, ensuring a swift response to threats and facilitating territorial expansion.
One notable example of strategic road use is the Via Appia, often referred to as the ‘Queen of Roads’. It was crucial during the Second Samnite War, providing a direct route for troops to move swiftly to the southern regions of Italy. Such roads were not only vital for conquests but also served as defensive lines, allowing the Roman army to reinforce vulnerable areas quickly.
Moreover, the roads connected critical military outposts, ensuring that communication and supply lines were maintained efficiently. This connectivity was a key factor in the empire’s ability to sustain long campaigns and defend its expansive borders. Through strategic road planning, Roman infrastructure was not just a means of transport but a cornerstone of military dominance and territorial control.
Legacy of Roman Roads
The influence of Roman roads on modern infrastructure is profound and enduring. The engineering principles developed by Roman engineers, such as layered construction and effective drainage systems, laid the groundwork for contemporary road-building practices. Their innovative use of local materials, including the pioneering application of concrete, continues to resonate in modern construction methods.

Historians often remark on the “remarkable durability” of Roman roadways, which have lasted for centuries and, in some cases, are still in use today. This durability has set a precedent for the construction of long-lasting and reliable transportation networks worldwide.
Beyond their technical contributions, the historical importance of Roman roads lies in their role as catalysts for economic and cultural integration within the Roman Empire. They facilitated the movement of troops, goods, and ideas, helping to unify diverse regions under Roman rule. “Roman roads were the veins and arteries of the empire,” notes one historian, emphasizing their critical role in sustaining Roman dominance.
In essence, the legacy of Roman roads is twofold: they are both a testament to historical ingenuity and a foundation upon which modern transportation infrastructures have been built.

Conclusion and Summary
In conclusion, Roman roads were a cornerstone of the empire’s military prowess and economic vitality. The strategic network of roads facilitated rapid troop movements, efficient communication, and robust trade routes. Key roads like the Via Appia exemplified the dual role of military logistics and economic expansion.
Employing advanced engineering techniques, such as layered construction and effective drainage, these roads were built to last. The use of local materials, diligent maintenance, and standardized construction further contributed to their enduring legacy.
Ultimately, Roman roads not only supported military conquests but also laid the groundwork for modern infrastructure, underscoring their historical and engineering significance.
FAQ on Roman Roads
- What were Roman roads primarily used for? Roman roads were crucial for military expansion, enabling rapid troop movement and efficient communication across the empire. They also supported trade and economic growth by connecting cities and provinces.
- How were Roman roads constructed? Roman road construction involved layered techniques. This included a foundation of large stones, followed by smaller stones and gravel, topped with tightly packed stones or paving slabs. This method ensured durability and effective drainage.
- Did the Romans invent concrete for road construction? While the Romans did not invent concrete, they did innovate its use. They used a form of concrete which included pozzolana (volcanic ash), enhancing the roads’ strength and resilience.
- Is it true Roman roads were always straight? While Roman roads were planned to be as straight as possible, engineers prioritized minimizing obstacles. This sometimes resulted in curved routes to navigate difficult terrain.
- Why have some Roman roads lasted so long? The longevity of Roman roads is attributed to innovative engineering, high-quality materials, and regular maintenance. These factors contributed to their enduring presence in modern landscapes.

