The ingenuity of Roman engineering is a hallmark of their enduring empire. At the core of Roman success lay an expansive network of roads and bridges, which served as the backbone of their infrastructure. This network was not merely a means of transportation; it was a strategic tool that enabled the empire to thrive.
The Roman Empire’s reliance on such infrastructure allowed for efficient movement of goods, people, and military forces, which was vital for maintaining control over vast territories. Roads like the Via Appia and bridges such as the Puente Romano were more than just feats of engineering. They were lifelines that connected distant provinces and facilitated economic and cultural integration.
This article will delve into the construction techniques and innovations that made Roman infrastructure a cornerstone of their empire, exploring how these ancient practices continue to influence modern transportation networks.
Innovations in Roman Road Construction
Materials
The construction of Roman roads, such as the Via Appia, relied on carefully selected materials to ensure durability and longevity. The roads were typically composed of a foundation of leveled earth, followed by layers of crushed rocks. The surface was completed with neatly arranged blocks made from various materials, designed to withstand extensive use. This multi-layered approach provided the necessary flatness and drainage to endure the test of time.

Techniques
Roman engineers employed innovative techniques to create roads that were not only durable but also efficient for travel. A notable method was the use of straight paths, facilitated by surveyors employing sighting poles to determine the most direct routes. As a historical source notes, “The Via Appia was designed with straight segments to minimize travel time and enhance surveying accuracy.” This design was complemented by a crown and adjacent ditches for water drainage, which prevented flooding in rainy regions.
The Via Appia, constructed in 312 BC, exemplifies these innovations, serving as a critical artery for military and commercial activities. Its enduring presence today underscores the advanced engineering practices that have influenced modern infrastructure development.
Roman Bridge Engineering
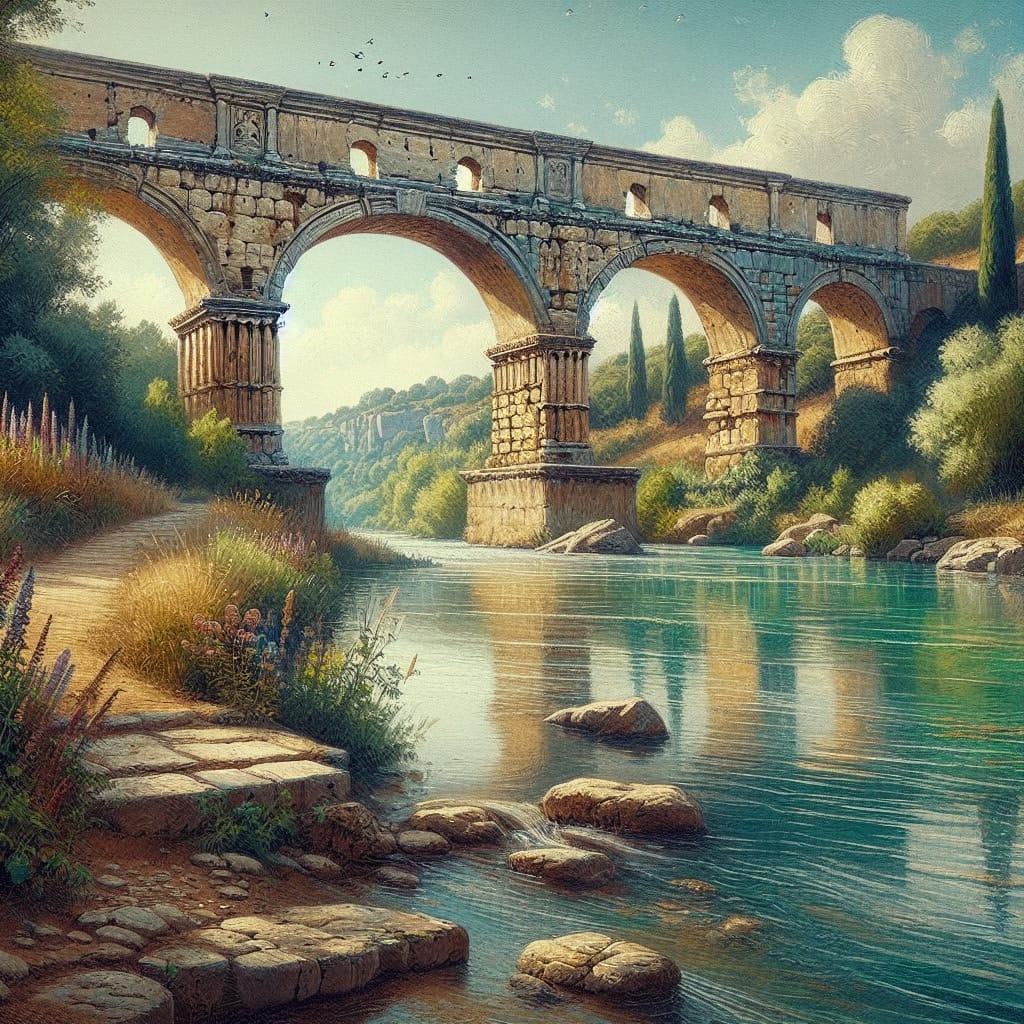
The construction of Roman bridges was a testament to the ingenuity of Roman engineers, who utilized innovative materials and design techniques. A key material was pozzolana, a type of mortar composed of water, sand, lime, and volcanic rock, which provided remarkable resistance to erosion. This enabled the creation of durable structures that could withstand the test of time.

- Use of pozzolana mortar for enhanced durability
- Incorporation of arches for optimal weight distribution
- Reliance on locally sourced stones and imported volcanic rock
The design of Roman bridges often featured arches, a revolutionary architectural element that distributed load forces along the curve, enhancing strength and stability. This technique was evident in structures such as the Limyra and Alcántara bridges.
Examining the Puente Romano offers insight into the legacy of Roman engineering. Although primarily known today as a luxury establishment in Marbella, the bridge itself remains a symbol of historical and architectural heritage, reflecting the enduring influence of Roman design principles.
| Bridge | Key Features | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Limyra Bridge | 26 segmental arches | Turkey |
| Alcántara Bridge | Preserved masterpiece | Spain |
| Puente Romano | Symbol of heritage | Spain |
The Role of Arches in Roman Engineering
Arches revolutionized Roman engineering, allowing for the construction of longer spans than traditional stone beams could support. The circular arch form was central to this development, enabling bridges and aqueducts to traverse vast distances with enhanced durability. This was achieved through the physics of the arch, which distributes loads evenly along its curve, channeling forces into the ground at the base. This design not only allows for greater spans but also increases the longevity of structures.
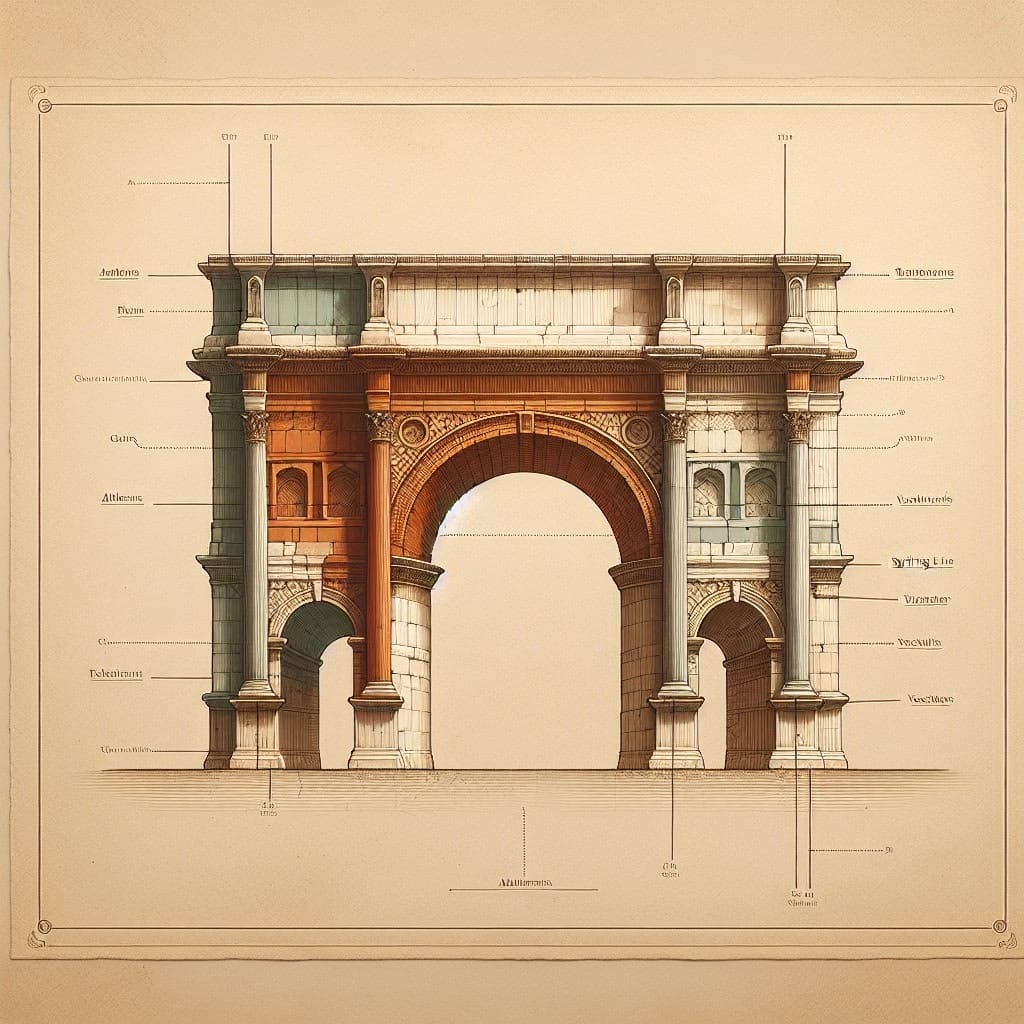
The strategic use of arches had profound implications for trade and military movement across the Roman Empire. By facilitating the construction of robust infrastructure, such as bridges and roads, arches enabled the efficient transportation of goods and military personnel. This infrastructure ensured that the empire could maintain its expansive territories and respond swiftly to threats. The Pont du Gard and Alcántara Bridge are exemplary structures that illustrate the Romans’ ability to combine functionality with engineering elegance. In doing so, they laid the groundwork for modern transportation networks, highlighting the enduring legacy of Roman arches.
Economic Impacts of Roman Infrastructure
The vast Roman infrastructure was instrumental in facilitating extensive trade across the empire. The transportation networks, which included approximately 80,000 kilometers of paved roads and 25,000 kilometers of inland waterways, enabled efficient movement of goods and people. This connectivity was crucial, as studies have shown that a 1% increase in effective distance reduced interregional trade volume by 2.4%.

Roman infrastructure also played a pivotal role in the economic integration of the empire. Key economic benefits of this integration included:
- Enhanced inter-regional trade, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Promotion of economic specialization and growth, with regions producing specific goods like Egyptian wine and Spanish olive oil.
- Stimulation of financial systems, enabling merchants to operate across diverse markets.
Moreover, the Roman state’s control over trade through systems like the annona ensured a stable supply of essential goods, further fostering economic resilience. This robust infrastructure not only unified the empire but also laid the groundwork for modern economic systems, influencing connectivity and trade patterns long after the fall of Rome.
Military Advantages Provided by Roads and Bridges
The Roman infrastructure was not only pivotal for trade but also served as a strategic military asset. The extensive road network enabled the rapid deployment of troops across the vast empire, ensuring that Roman legions could swiftly respond to threats and maintain control over distant territories. This capability was crucial during the Second Punic War, where the mobility of Roman forces played a decisive role in countering Hannibal’s advances.

Furthermore, Roman bridges, such as the iconic Puente Romano, facilitated strategic positioning by allowing armies to cross formidable natural barriers like rivers. These structures not only exemplified engineering prowess but also represented tactical advantages. As military historian Liddell Hart noted, “The power to control movement is the power to control the battle.”
In essence, Roman roads and bridges were more than mere infrastructure; they were integral to the empire’s military strategy, ensuring that Roman forces could be both agile and effectively positioned, a feat that contributed significantly to the empire’s enduring dominance.
Influence on Modern Transportation Networks
The enduring legacy of Roman engineering is prominently visible in modern transportation networks. **Roman road construction techniques** have been adapted to today’s infrastructure, emphasizing durability and efficiency. Modern roads, much like their Roman predecessors, prioritize solid foundations using layered materials to enhance stability and longevity.

Surveying and route planning have evolved from Roman methodologies, ensuring optimal paths for highways and minimizing natural obstacles. The categorization of roads into types—public, military, and local—continues in contemporary infrastructure, addressing diverse traffic needs.
Modern examples like the **Interstate Highway System** in the United States echo Roman principles. This network mirrors Roman roads in its strategic spread and maintenance practices, with toll systems akin to those employed by the Romans.
| Feature | Roman Roads | Modern Highways |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Large rocks and sand | Layered materials |
| Drainage | Cambered surface | Advanced drainage systems |
| Traffic Separation | Pedestrian walkways | Sidewalks and bike lanes |
The Roman influence is also evident in bridges, where the use of arches remains prevalent. This ancient technique is employed for its structural strength, as seen in modern structures like the Sydney Harbour Bridge.
Roman Construction Techniques
The Romans were pioneers in engineering, particularly in their road construction techniques. A key element of their success was the layering method, which involved a meticulous process to ensure durability and stability. The process began with a base layer of large stones, meticulously laid to form a solid foundation. This base was then covered with smaller stones and sand, creating a compact layer that would enhance the road’s strength.
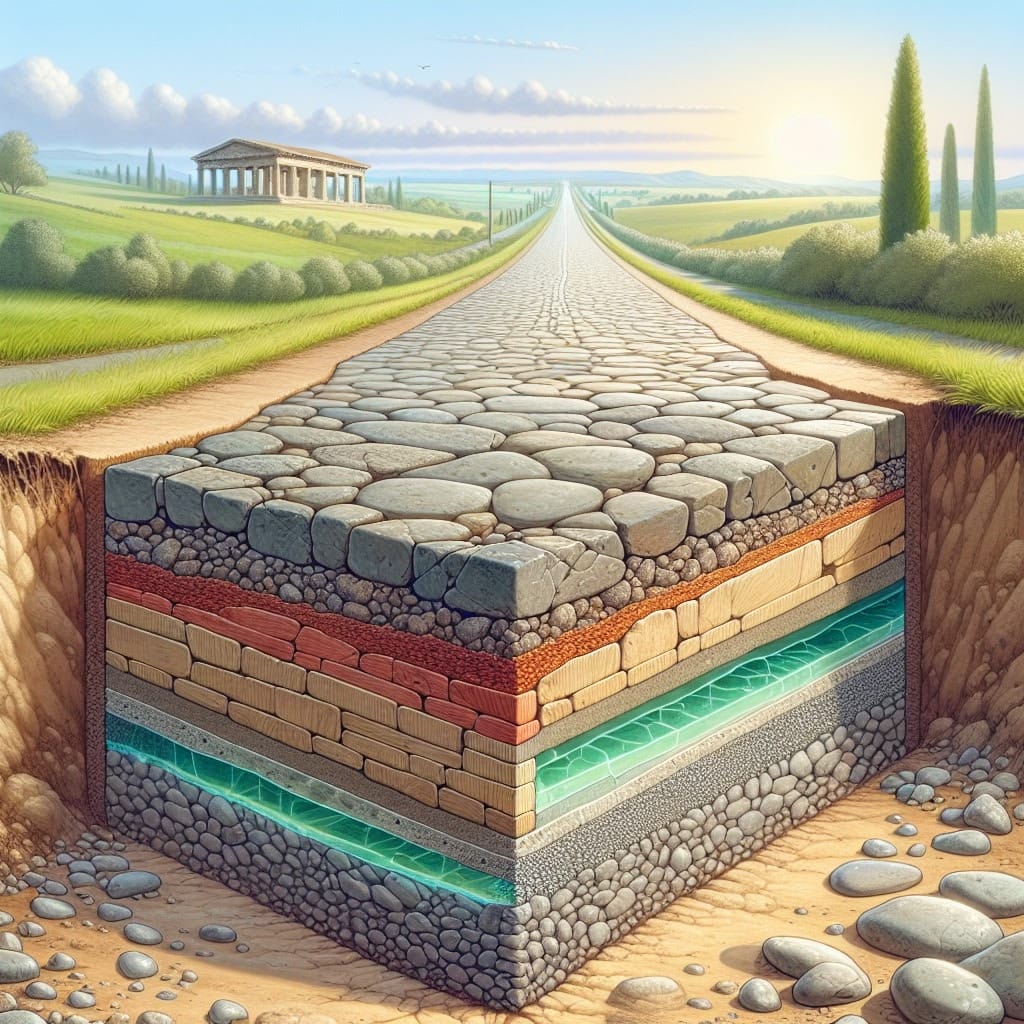

Above the compacted stones, the Romans placed tightly fitted paving stones, which provided a smooth, durable surface for travel. This multi-layered approach not only improved load distribution but also facilitated the drainage of water, preventing erosion and damage.
Another significant innovation was the use of Roman concrete, made from a mixture of lime and volcanic ash, known as pozzolana. This material set underwater, providing a robust and enduring solution for both roads and bridges. Roman concrete was particularly renowned for its resilience, allowing structures to withstand the test of time.
The strategic use of these techniques underscored the Romans’ ability to build an infrastructure that supported their expansive empire, influencing modern construction practices to this day.
Legacy of Roman Engineering Practices
The enduring legacy of Roman engineering is evident in the many long-lasting structures that remain in use today. Iconic examples such as the Colosseum in Rome and the Pont du Gard in France showcase the Romans’ advanced understanding of architecture and design. These structures not only highlight the durability of Roman construction techniques but also continue to attract admiration for their architectural brilliance.

The influence of Roman engineering extends beyond their physical structures to the realm of education. Roman methodologies have been integrated into modern architectural curricula, providing students with a foundation in engineering principles that emphasize durability, functionality, and aesthetics. These principles are mirrored in contemporary infrastructure projects, where the Romans’ use of arches and concrete remains integral to modern engineering education.
Through these educational frameworks, the Romans’ innovations continue to inspire and inform engineers and architects around the world. This lasting impact underscores the timeless nature of Roman engineering, ensuring their practices remain relevant in shaping the built environment of today and tomorrow.
Cultural and Social Impacts of Infrastructure
The Roman Empire’s extensive network of roads and bridges played a pivotal role in the unification of diverse regions across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. By providing a reliable means of transportation, these infrastructures facilitated the movement of people, goods, and ideas, thereby promoting cultural exchange and integration. Merchants, scholars, and travelers carried with them not only goods but also philosophies, technologies, and artistic influences that enriched the areas they visited.

Furthermore, the roads and bridges contributed to the spread of Roman culture and societal norms. Roman law, language, and architecture became prevalent in conquered territories, creating a sense of shared identity among disparate communities. The infrastructure enabled the efficient administration of these vast regions, ensuring that Roman customs and governance were consistently implemented.
This integration fostered social cohesion, as the people within the empire experienced a unified cultural landscape, underscored by the physical presence of Roman engineering. The enduring influence of these infrastructures can be seen in modern transportation networks, which continue to connect diverse populations and facilitate cultural interactions across the globe.
Challenges in Roman Infrastructure Projects
The Roman Empire’s ambitious infrastructure projects were met with numerous geographical challenges that demanded innovative engineering solutions. Surveyors meticulously plotted routes to navigate valleys, mountains, swamps, and rivers, ensuring roads maintained a direct path. Bridges and tunnels were strategically employed to traverse these natural obstacles, often utilizing the arch design to support expansive crossings and maintain structural integrity.

Environmental challenges were equally significant, particularly in densely populated urban centers. Romans adeptly managed air and water pollution through extensive aqueduct systems and strategic placement of industries to minimize their impact on residential areas. These measures reflected an early appreciation for environmental health and resource sustainability.
- Resource Allocation: The management of resources required a collaborative approach, involving various political and social actors. Aediles and censors played key roles in overseeing public works and maintenance.
- Labor and Funding: Initially reliant on citizen labor, Rome transitioned to utilizing slaves and precious metals for funding, marking a shift towards a more capitalistic resource management system.
Despite these challenges, Roman infrastructure projects stood as testaments to their engineering prowess, laying the groundwork for modern urban planning and resource management practices.
Technological Innovations in Roman Construction
The Roman Empire’s architectural and engineering feats were propelled by an array of innovative tools and machinery. These advancements enabled the construction of enduring structures that continue to inspire modern engineering.

- Tools: Romans used the groma for surveying, enabling them to establish straight lines and right angles, crucial for road and aqueduct construction. The chorobates, a water level, ensured precision in aqueduct gradients.
- Machinery: Cranes, often powered by human or animal labor, facilitated the lifting of heavy stones, while pile drivers allowed for the construction of sturdy foundations in challenging terrains.
Roman engineering breakthroughs included the widespread use of concrete, composed of lime mortar, water, and volcanic ash. This durable material was pivotal in constructing large structures like the Pantheon and bridges.
Arches, another engineering marvel, supported expansive spans, significantly enhancing the load-bearing capacity of bridges and aqueducts. These innovations not only advanced Roman construction but also laid foundational principles for modern infrastructure design, exemplifying the enduring legacy of Roman engineering prowess.

Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy
The Roman Empire’s infrastructure, epitomized by its roads and bridges, was a cornerstone of its dominance. Through advanced surveying, strategic resource management, and innovative construction techniques, the Romans overcame geographical and environmental challenges. Their use of arches and concrete laid the foundation for structures that have withstood millennia.
Reflecting on the lasting impact, Roman engineering principles continue to influence modern infrastructure, inspiring sustainable designs and efficient urban planning. As we look to the future, the Roman legacy serves as a testament to the enduring power of innovation and adaptability in engineering.
FAQ on Roman Infrastructure
Roman infrastructure has left a profound legacy, sparking curiosity and misconceptions. Here are some common questions answered:
Q: How were Roman roads constructed to withstand the test of time?
A: Roman roads were built using a sophisticated layering method. This method involved multiple layers of materials, including stones, gravel, and sand, topped with tightly-fitted paving stones. Their elevated design and drainage systems helped maintain their durability in various weather conditions.
Q: Did Romans really invent the arch used in bridges?
A: While the Romans did not invent the arch, they perfected its use in bridge construction. By incorporating arches, they enabled longer spans, crucial for both trade and military movement across vast distances.
Q: Were all Roman roads straight?
A: It is a misconception that all Roman roads were straight. While Romans preferred straight paths to reduce travel time, they meticulously surveyed for optimal routes, adapting to natural landscapes, such as mountains and rivers, by building bridges and tunnels.
This exploration of Roman infrastructure highlights the ingenious methods and careful planning that have influenced modern engineering practices.

