The Roman Empire is renowned for its architectural and engineering achievements, with its infrastructure serving as a cornerstone of its historical significance. Roads, bridges, and aqueducts not only facilitated commerce and military movements but also enhanced urban living.
This article delves into the techniques Romans employed to ensure their infrastructure’s longevity. By exploring their innovative use of materials and design principles, we uncover how these ancient practices continue to inspire modern engineering solutions.
Durable Materials
Central to the Roman Empire’s enduring infrastructure were the strategically chosen materials of stone and Roman concrete. The Romans utilized volcanic rocks such as tuffs and travertine, known for their resistance to wear and environmental factors. These stones, sourced from local quarries, were integral to Roman architecture due to their durability and suitability for construction. Historic structures like the Colosseum and the Roman Forum exemplify the effective use of these materials, showcasing their long-term resilience in urban settings.

Equally significant was the use of Roman concrete, which incorporated pozzolanic materials, such as volcanic ash, for its exceptional durability. This concrete was further enhanced by the inclusion of lime clasts, offering a self-healing mechanism that preserved the integrity of structures over centuries. The Pantheon serves as a testament to the strength of Roman concrete, still standing after more than two millennia. The innovative blend of materials ensured Roman constructions could endure harsh environmental conditions, from seismic activity to coastal erosion, underscoring the Romans’ advanced understanding of material science.
Innovative Design Principles
The Roman approach to infrastructure was characterized by a visionary design philosophy that prioritized sustainability and long-term usability. Roman engineers crafted structures with an eye towards enduring utility and durability, ensuring that their creations would serve generations to come. This commitment to sustainability is evident in their use of pozzolanic material in Roman concrete, which not only enhanced the strength of their constructions but also imbued them with a self-healing mechanism that maintained structural integrity over time.
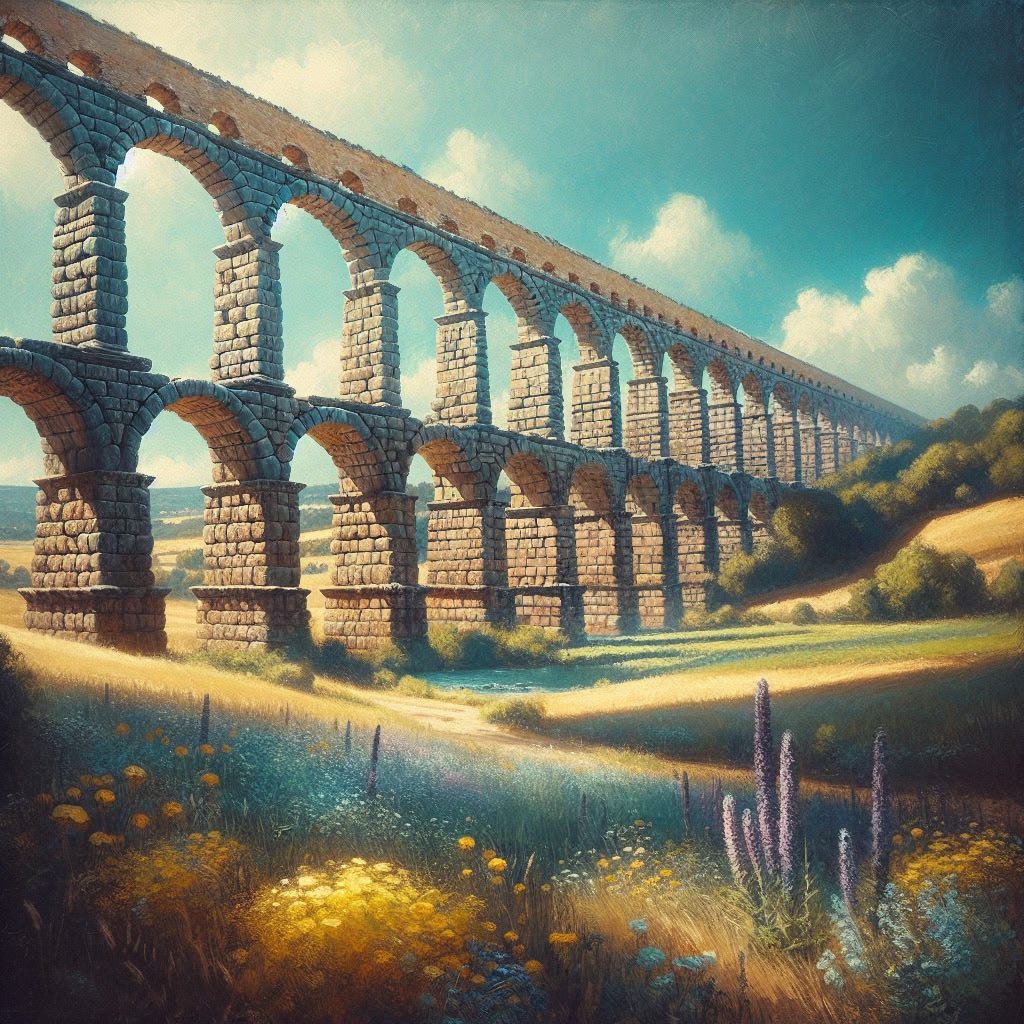

Beyond mere functionality, Roman infrastructure was also a testament to the integration of aesthetics. Roads and aqueducts were not only designed to facilitate efficient transport and water supply but were also constructed with an architectural grace that harmonized with the surrounding landscape. Aqueducts, in particular, were engineering marvels that combined utility with grandeur, their arches and spans becoming iconic symbols of Roman architectural ingenuity. Such integration of form and function underscored a holistic approach to design, where aesthetics were not sacrificed for practicality, but rather enhanced the overall effectiveness and cultural impact of the infrastructure.
Regular Maintenance Practices
In the Roman Empire, the systematic scheduling of inspections and repairs was pivotal to the enduring reliability of their infrastructure. Under the watchful eyes of aediles and censors, public works were meticulously maintained, with contractual obligations ensuring a continuous cycle of upkeep. This formalized system was supported by public funds, allocated by the Senate, to address the maintenance needs of roads, bridges, and aqueducts. The strategic use of mile markers on roads further exemplified this organized approach, recording the responsibility of specific individuals or communities for different sections of upkeep.

Technological advancements in Roman engineering played a significant role in their maintenance practices. The use of the arch, a hallmark of Roman architectural prowess, allowed for sturdier structures that required less frequent repairs. Innovations in construction techniques, such as the development of robust materials like Roman concrete, further enhanced the longevity of their infrastructure. By integrating these engineering principles, the Romans crafted a legacy of enduring structures, showcasing their commitment to both innovation and sustainable maintenance.
Organizational Structure for Maintenance
The maintenance of Roman infrastructure was a meticulously organized endeavor, involving both state and local authorities. At the apex of this hierarchy were the aediles and censors, who played pivotal roles. Aediles enforced maintenance protocols, while censors oversaw the financing of public works, ensuring a well-structured oversight system was in place.
Funding for these maintenance activities was derived from public taxes, appropriated by the Roman Senate to support ongoing infrastructure projects. This financial strategy underscored a keen awareness of resource allocation, ensuring regular inspections and repairs. Such a system facilitated a sustainable approach to infrastructure longevity, as documented in surviving contract documents like the lex pareti faciendo.
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Aediles | Enforcement of maintenance policies |
| Censors | Management and financing of public works |
| Contractors | Execution and upkeep of infrastructure |
This strategic combination of official oversight, contractual obligations, and public funding formed the backbone of Rome’s infrastructure maintenance, reflecting a sophisticated approach to ensuring the empire’s enduring legacy.
Case Study: Roman Roads
The construction of Roman roads exemplified advanced engineering techniques that ensured their durability and functionality for centuries. These roads were meticulously planned, with a focus on straight path construction to connect key points efficiently. Roman engineers managed slopes by maintaining an 8% maximum incline, facilitating smooth movement for animal-drawn vehicles. The roads were layered with materials like gravel and stone, providing resilience against heavy traffic. Additionally, tools such as the dioptra and groma were employed to ensure precision in alignment and leveling, further aiding in the roads’ long-lasting nature.

Historically, the impact of these roads was profound, as evidenced by the vast network spanning over 400,000 kilometers. This network facilitated efficient military logistics and economic trade, contributing significantly to the cohesion and expansion of the Roman Empire. The enduring nature of Roman roads is illustrated by modern examples like the Via Appia Antica, which remains partially in use today. These roads not only served immediate needs but also left a lasting legacy, influencing contemporary road construction worldwide, highlighting Roman engineering prowess and strategic foresight.
Engineering Marvels: Roman Bridges
The Roman Empire’s engineering feats are epitomized by their bridges, which stand as testaments to their architectural innovation. Utilizing a revolutionary circular arch form, Roman engineers achieved greater spans and permanence than traditional wooden structures. A key technique was the use of pozzolana, a volcanic mortar that bolstered the structural integrity of bridges, making them resistant to erosion and time. This innovation, alongside the circular arch, facilitated the construction of enduring structures.

Among the notable Roman bridges, the Ponte Vecchio stands out as the first segmental arch bridge in the Western world, designed to allow free passage of floodwaters. Another marvel, the Rialto Bridge, showcases a single central arch, avoiding multiple arches that could hinder traffic, a testament to both form and function. The Sant’Angelo Bridge, constructed over 1,800 years ago, exemplifies the use of cofferdam foundations, enhancing its durability.
Historical texts emphasize, “the strength of piers became critical,” highlighting the ingenuity behind these structures. Roman bridges not only served practical needs but inspired modern engineering, reflecting a legacy of durability and innovation that continues to influence contemporary infrastructure.
Aqueducts: Lifelines of Roman Cities
Roman aqueducts were pivotal to the empire’s urban development, serving as the backbone for public health and urban expansion. By providing a reliable supply of clean water, they supported the daily needs of burgeoning populations, bolstering the growth of cities like Rome. The impact of these aqueducts extended beyond mere utility; they enhanced public health, enabled sanitation, and supported economic activities that relied on a consistent water supply.

The construction of Roman aqueducts was a testament to advanced engineering. Initiated with the Aqua Appia in 312 B.C., these structures were primarily built underground to protect against potential threats. Roman engineers employed instruments like the groma for precise alignment, ensuring a consistent downward slope that capitalized on gravity to maintain water flow. These channels were often lined with stone and clay, reflecting a sophisticated understanding of material use and structural integrity. Such meticulous planning and design allowed for the establishment of aqueducts throughout the empire, facilitating the spread of Roman influence and infrastructure.
Modern Parallels in Infrastructure
Roman engineering principles continue to influence contemporary infrastructure development, offering timeless lessons in construction and urban planning. One notable parallel is detailed planning. Just as Romans meticulously designed structures like the Library of Celsus in Ephesus, modern projects emphasize comprehensive planning to enhance efficiency and sustainability.

Another key area is the use of natural materials. Romans utilized materials such as local marble, which modern architects mirror by prioritizing locally-sourced, environmentally-friendly resources to improve energy efficiency. Additionally, Roman techniques in road construction and maintenance continue to inform today’s infrastructure, particularly in Italy, where ancient road networks influence the layout of contemporary highways and railways.
Modern urban planning also reflects Roman insights in density management and mixed-use development. By fostering high-density living and integrating commercial spaces within residential areas, cities today reduce reliance on cars and promote sustainable lifestyles—concepts deeply rooted in Roman urban design.
Global Influence of Roman Infrastructure
Roman engineering techniques have reached far beyond the borders of the ancient empire, leaving a lasting imprint on modern infrastructure worldwide. As Romans expanded their domain, they introduced advanced construction methods that laid the groundwork for European engineering practices. Roman roads and aqueducts set precedents in durability and design, influencing transport networks across Italy and beyond.
These techniques were not only adopted but also adapted to fit diverse cultural contexts. In Britain, Roman roads became the backbone of the country’s transport system, while in France, the Roman aqueduct at Pont du Gard inspired subsequent water management systems. The practice of utilizing local materials, a hallmark of Roman construction, continues to inform sustainable building practices globally.
Moreover, the Roman emphasis on urban density and mixed-use development has shaped contemporary urban planning, promoting walkable cities that reduce car dependency. This cross-cultural exchange of ideas underscores the enduring legacy of Roman infrastructure, illustrating its profound impact on the modern world.
Historical Studies on Roman Engineering
Roman engineering has long captivated scholars, drawing continuous academic interest due to its profound impact on infrastructure and urban development. The meticulous design and planning processes employed by Roman architects have provided a rich field of study, revealing insights into the advanced techniques that enabled the construction of enduring structures like roads, aqueducts, and amphitheaters.

Recent discoveries continue to shed light on Roman engineering marvels. For instance, ongoing excavations and research into the Roman road networks in Italy have uncovered methods of construction that emphasize strategic planning and geographical considerations, highlighting their influence on modern infrastructure. Such studies provide empirical evidence of how Roman engineering principles still inform contemporary practices.
Moreover, the preservation of ancient sites like the Library of Celsus in Ephesus offers valuable lessons on the use of natural materials and sustainable building practices. This ongoing academic engagement not only enriches our understanding of Roman contributions but also inspires modern innovations, ensuring that the legacy of Roman engineering endures in contemporary infrastructure.
Challenges in Preserving Roman Infrastructure
Preserving Roman infrastructure poses significant challenges, influenced by both environmental and human factors. The ravages of time, such as erosion, weathering, and seismic activity, continually threaten the structural integrity of ancient roads, bridges, and aqueducts. Human activities, including urban development and tourism, can also contribute to the degradation of these historical sites. For instance, modern infrastructure projects sometimes intersect with ancient routes, potentially leading to their alteration or destruction. The need to balance preservation with contemporary urban needs presents a complex dilemma for planners and conservationists alike.
Efforts to maintain and restore these ancient structures are multifaceted and ongoing. Advanced technologies, such as digital mapping and 3D reconstruction, are increasingly employed to understand and repair ancient Roman infrastructure. Organizations dedicated to heritage conservation collaborate with governments and local communities to ensure these structures are preserved for future generations. Furthermore, initiatives focused on sustainable tourism aim to minimize the impact of human activity, while educational programs raise awareness about the historical significance of Roman engineering. These efforts collectively strive to protect the enduring legacy of Roman infrastructure.
Conclusion
In summary, the Roman Empire’s commitment to innovative engineering and meticulous maintenance set a precedent for enduring infrastructure. Their use of durable materials, strategic planning, and regular upkeep ensured their structures stood the test of time. Modern infrastructure projects continue to draw inspiration from these ancient techniques, emphasizing the Romans’ profound impact. As we integrate these principles into contemporary practices, we honor a legacy that fundamentally shaped our urban landscapes and continues to guide sustainable development today.
FAQs
As we delve into the remarkable infrastructure of the Roman Empire, several common questions arise about their enduring legacy and techniques.
- What materials did the Romans use for their infrastructure? The Romans primarily used durable materials like stone and Roman concrete, known for their longevity and resistance to environmental wear.
- How did Roman roads influence modern infrastructure? Roman roads have significantly shaped modern infrastructure, particularly in Italy, where their strategic planning and engineering techniques continue to inform contemporary road and railway designs.
- What role did maintenance play in Roman infrastructure? Regular maintenance was crucial. The Romans conducted scheduled inspections and repairs to ensure the longevity of their roads, bridges, and aqueducts, a practice mirrored in today’s infrastructure maintenance strategies.
- Are there modern parallels to Roman construction techniques? Yes, modern projects often draw from Roman principles such as detailed planning, use of local materials, and density management in urban planning.
These insights highlight how Roman engineering continues to inspire and inform contemporary infrastructure efforts worldwide.

