Frescoes from Pompeii and Herculaneum are invaluable artifacts that offer a unique glimpse into the vibrant life of ancient Romans. These artworks serve as windows into both public and private experiences, depicting everything from idyllic landscapes to religious rites. Understanding these frescoes is essential for anyone interested in Roman culture because they encapsulate significant aspects of daily activities, social customs, and religious practices.
The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 C.E. was a catastrophic event that resulted in the burial of these cities under layers of ash and rock. This natural disaster ultimately preserved not only the structures but also these remarkable frescoes for centuries. The layers of volcanic material created an airtight seal around the artworks, allowing them to retain their color and detail remarkably well over time.
In addition to their aesthetic appeal, these frescoes showcase the technical prowess of Roman artists. Utilizing a technique known as true fresco, pigments were applied onto wet plaster. As the plaster dried, the colors bonded with the wall—ensuring vibrancy and durability that has lasted through the ages.
This article will explore how frescoes from Pompeii and Herculaneum illuminate various aspects of Roman life. By examining their artistry and themes, we will gain insight into a civilization rich in cultural values and traditions. Through this exploration, you will appreciate why these frescoes are not merely art but vital historical documents that continue to inform our understanding of ancient Rome.

The Historical Context of Pompeii and Herculaneum
The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 C.E. was a significant event in history. It destroyed the thriving cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum, burying them under thick layers of volcanic ash and pumice. This created a unique time capsule that preserved many aspects of Roman civilization. The force of the eruption also changed the landscape, leaving behind an eerie but priceless archaeological site.
Description of the Eruption and Burial
The eruption unfolded over two days, releasing a cloud of stones, ashes, and fumes to a height of 33 kilometers (20.5 miles).
- The initial blast was followed by pyroclastic flows—hot gas and volcanic matter that swept through the towns at incredible speeds.
- Buildings crumbled under the weight of ash, while thermal shock caused roofs to collapse.
- This rapid burial insulated artifacts, including frescoes, from exposure to air and moisture, significantly contributing to their preservation.
The aftermath left both Pompeii and Herculaneum encased in this geological tomb. Centuries later, archaeological efforts unearthed these sites, revealing insights into daily life during the Roman Empire.
Importance as Archaeological Sites
Pompeii and Herculaneum are crucial for understanding Roman life and art for several reasons:
- Cultural Insights: The preserved frescoes illustrate not only artistic techniques but also social customs, religious practices, and family dynamics.
- Architectural Significance: Structures like villas, baths, and temples showcase Roman architectural ingenuity.
- Social Stratification: Excavations reveal distinct societal layers through residential areas ranging from opulent homes to modest dwellings.
The archaeological significance of these sites cannot be overstated. They provide essential data for historians and archaeologists who study ancient Rome. Discoveries such as public squares bustling with activity or intimate domestic scenes reflect the vibrancy of Roman culture.
In addition to the artistic treasures found within these walls, the preservation methods employed by natural forces grant us a rare glimpse into everyday Roman existence. Each fresco tells a story—a narrative woven into the fabric of time that continues to captivate modern audiences. Understanding this historical context enhances appreciation for the frescoes’ role in illuminating ancient customs and beliefs.
As research progresses, scholars continue to unlock further secrets held within these remarkable sites, ensuring their legacy endures for generations to come.
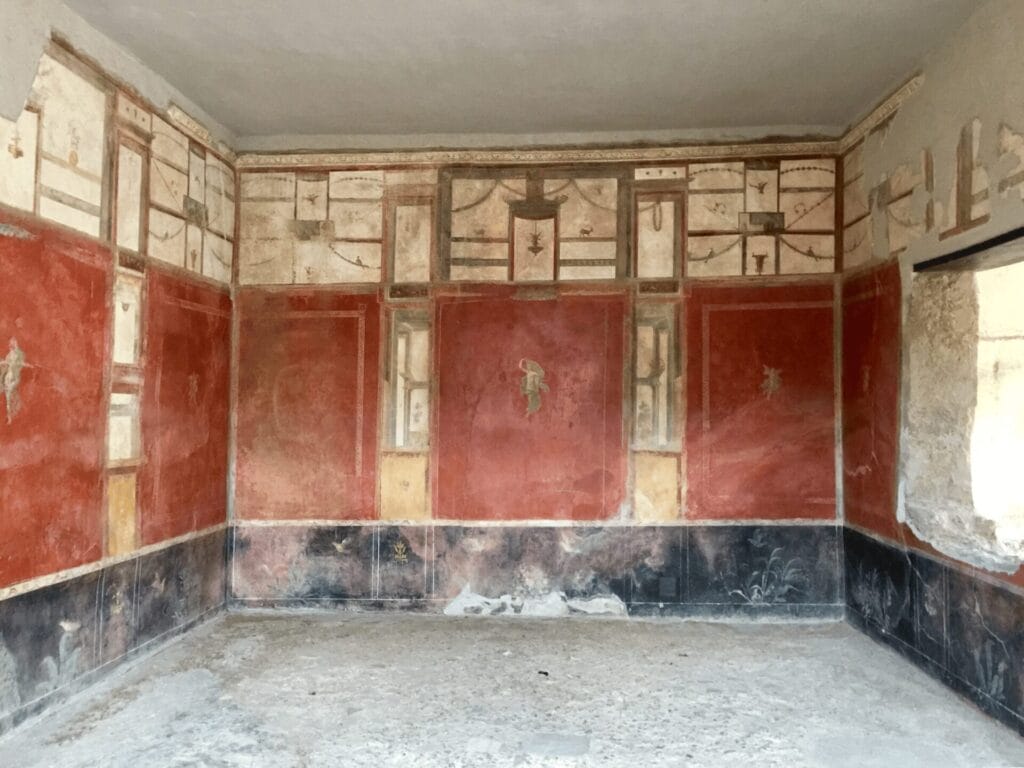

The Artistry Behind Roman Frescoes
Frescoes from ancient Rome are remarkable not only for their content but also for the sophisticated techniques employed by artists. Central to this artistry is the true fresco technique, a method that involves applying pigments onto wet plaster. This approach allowed colors to bond with the wall as it dried, resulting in artworks that boast both vibrant colors and exceptional longevity.
Advantages of True Fresco Technique
The true fresco technique offers several advantages that contribute to the enduring beauty of Roman frescoes:
- Color Vibrancy: The wet plaster absorbs the pigments, creating a chemical reaction that enhances color saturation. Unlike other painting methods, which might fade over time, true frescoes maintain their brilliance for centuries.
- Durability: Once dried, the fresco becomes an integral part of the wall, making it less susceptible to peeling or flaking compared to paintings on canvas or wood. This durability has been crucial in preserving these artworks through millennia.
Themes and Compositions in Roman Frescoes
The themes represented in Pompeian frescoes provide insights into various aspects of Roman life. Common motifs include:
- Landscapes: Many frescoes depict serene natural scenes, often featuring lush greenery, mountains, and water bodies. These landscapes not only served aesthetic purposes but also created a sense of tranquility within domestic spaces.
- Mythology: Mythological figures and stories frequently appear in these artworks, showcasing gods and goddesses engaged in various narratives. Such representations reflect the deep-seated beliefs and cultural values of Romans, emphasizing their connections to divine entities.
- Daily Life Scenes: A significant number of frescoes illustrate everyday activities, capturing moments of domestic life such as cooking, dining, and socializing. These depictions reveal social structures and family dynamics within Roman society.

The compositions themselves are dynamic and engaging. Artists employed techniques such as:
- Perspective: By manipulating perspective, artists created depth in their work, giving viewers an immersive experience that drew them into the scene.
- Color Schemes: Bold contrasts of colors were often used to highlight specific elements within a mural. This strategic use of color not only guided the viewer’s eye but also emphasized particular narratives or themes.
Example Murals
One notable example includes the Villa of the Mysteries, where elaborate frescoes depict initiation rites associated with Dionysus. The vivid color palette combined with intricate detailing allows viewers to perceive both movement and emotion within each figure.
Another example is found in the House of the Vettii, showcasing rich imagery of daily life intertwined with mythological elements. Here, you can observe how social status is reflected through decoration choices and thematic selections.
Roman frescoes serve as more than mere decoration; they encapsulate a vibrant culture’s ethos. Each piece is a testament to skilled craftsmanship and an enduring legacy that continues to inform our understanding of ancient Rome’s societal fabric.
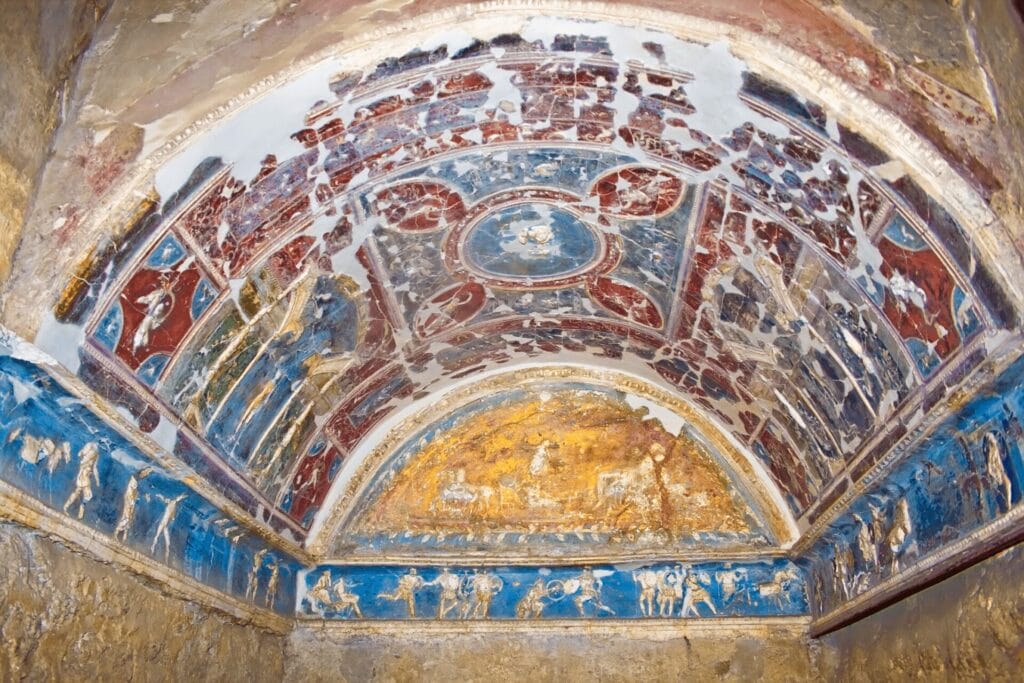

Exploring Themes Depicted in Pompeian Frescoes
Frescoes from Pompeii provide invaluable insights into domestic life in ancient Rome and the vibrant social customs of the time. These artworks serve as windows into the daily routines and communal interactions that characterized Roman society.
Domestic Life
Frescoes showcasing domestic activities reveal much about the family structure and roles within Roman households. Common themes include:
- Family Gatherings: Scenes depicting families engaged in various activities, such as dining or relaxing, highlight the importance of familial bonds.
- Household Chores: Murals illustrating daily tasks, like cooking or weaving, shed light on the everyday responsibilities of both men and women. These depictions reflect a society where family members played distinct yet complementary roles.
- Childhood Activities: Images of children playing or learning emphasize the value placed on education and play within family life.
These frescoes not only represent individual households but also mirror broader societal values regarding family dynamics and responsibilities.
Public Gatherings and Entertainment
Beyond private life, Pompeian frescoes showcase public gatherings that were central to Roman culture. The vibrant murals depict:
- Banquets: Lavish feasts featured prominently in many frescoes, portraying the significance of food and hospitality in social interactions. Guests are often shown reclining at tables, enjoying food, wine, and entertainment.
- Games and Festivals: Scenes from public events like gladiatorial games or religious festivals highlight community engagement. Such murals emphasize the role of entertainment in fostering social cohesion among Romans.
- Civic Life: Some frescoes depict officials or citizens participating in civic duties, reflecting the responsibilities of individuals within their communities.
These images provide a snapshot of how Romans engaged with one another during leisure time while reinforcing social hierarchies and communal bonds.
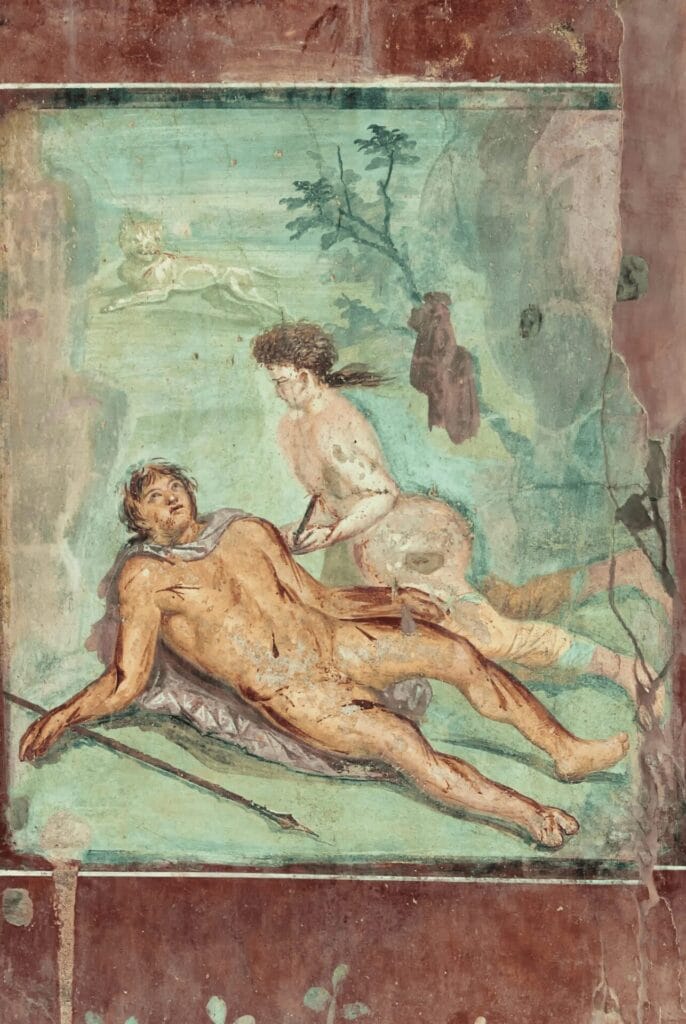

Artistic Techniques Enhancing Themes
The techniques employed by Roman artists further enhance these themes. The use of true fresco allowed for vibrant colors that brought scenes to life, contributing to their emotional depth. Key aspects include:
- Dynamic Compositions: Artists skillfully arranged figures to create a sense of movement and interaction among characters.
- Symbolism in Color: Colors were used intentionally; for example, red might symbolize excitement or passion during festivities, while cooler tones could convey tranquility during intimate family moments.
The artistry behind these frescoes not only elevates their aesthetic appeal but also enriches our understanding of Roman social customs through visual storytelling.
In a similar vein to Piero della Francesca’s spiritual art, which delves into profound themes through artistic expression, the frescoes from Pompeii serve as essential artifacts illuminating both public celebrations and private lives. As excavations continue to reveal more about these ancient artworks, each mural offers a deeper connection to the complexities of Roman culture, enriching our comprehension of their world.
Religious Beliefs Revealed Through Art: Mythology and Worship Practices in Pompeian Frescoes
Frescoes from Pompeii provide a vivid reflection of the religious life that permeated ancient Roman culture. The depiction of gods, rituals, and mythological themes in these murals offers profound insights into how religion influenced daily life, social structures, and individual identities.
Depictions of Deities and Myths
Pompeian frescoes frequently showcase a pantheon of Roman gods. The portrayal of deities such as Jupiter, Venus, and Bacchus reveals the significance of mythology in Roman society. For instance:
- Jupiter, often depicted wielding lightning bolts, symbolizes authority and power.
- Venus, associated with love and beauty, is shown in various scenes celebrating relationships and fertility.
- Bacchus, the god of wine, features prominently in festive settings, highlighting the cultural importance of wine in both social gatherings and religious rites.
These representations serve not only as decorations but also as reminders of divine presence in everyday lives. Many households included frescoes dedicated to household gods (Lares and Penates), emphasizing the belief that divine protection was essential for family well-being.
Rituals Captured in Art
In addition to depicting deities, Pompeian frescoes illustrate various worship rituals integral to Roman life. Scenes depicting sacrifices, feasts honoring the gods, or public festivals are common. These murals often include:
- Processions, where priests perform rituals with offerings.
- Ceremonial banquets, signifying communal worship where families come together to honor their deities.
The presence of such imagery underscores that religious practices were embedded in the social fabric of Roman communities. Engaging with these rituals was a means for Romans to connect with the divine and maintain favor among their gods.
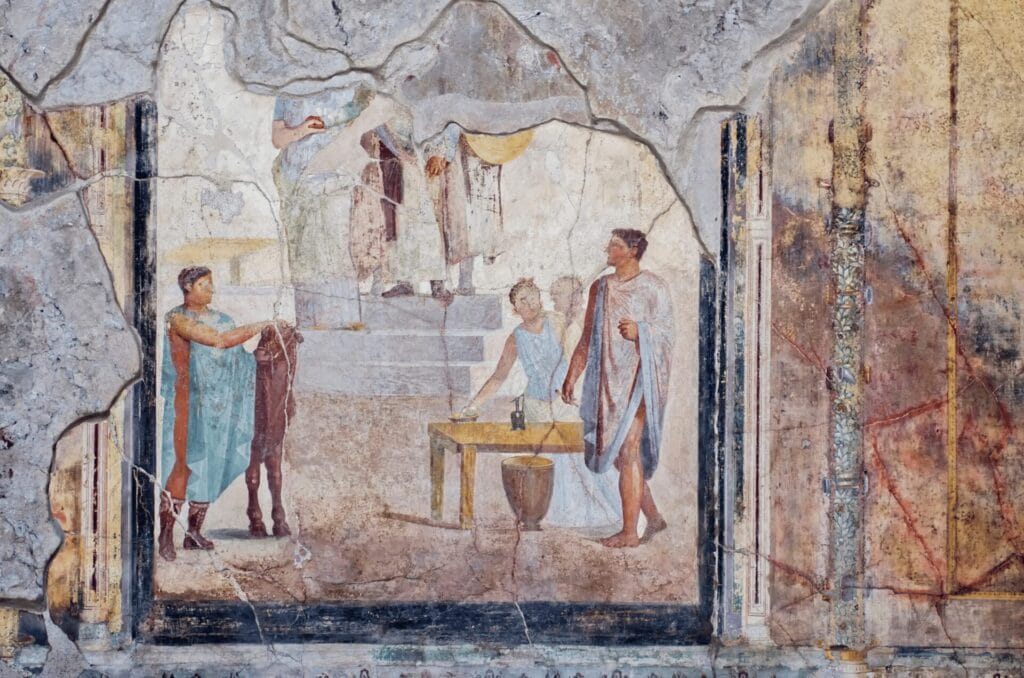

Significance of Religion in Daily Life
The significance of religion within Pompeii’s society is evident not just through imagery but through its pervasive influence on daily life. Religion shaped everything from personal identity to public affairs:
- Social Cohesion: Participation in religious festivals fostered community bonds. Public events brought citizens together, reinforcing shared beliefs and collective identity.
- Cultural Identity: Religious practices provided a sense of continuity amid changing political landscapes. Romans often turned to their gods for guidance during turbulent times.
- Moral Framework: Mythological narratives served as moral lessons that guided behavior and societal norms.
Understanding these aspects reveals how intrinsic religion was to the rhythms of daily life in ancient Rome.
The religious themes depicted in Pompeian frescoes present a multifaceted view of Roman life that transcends mere aesthetics. They highlight the deep-rooted connection between art and spirituality while illustrating how mythological themes shaped societal values and interactions.
As you explore these vibrant artworks, consider how they encapsulate not only the beliefs but also the lived experiences of those who walked the streets of Pompeii over two millennia ago. The frescoes stand as windows into a world where divinity intertwined seamlessly with human existence, offering an enduring legacy that continues to captivate modern audiences.
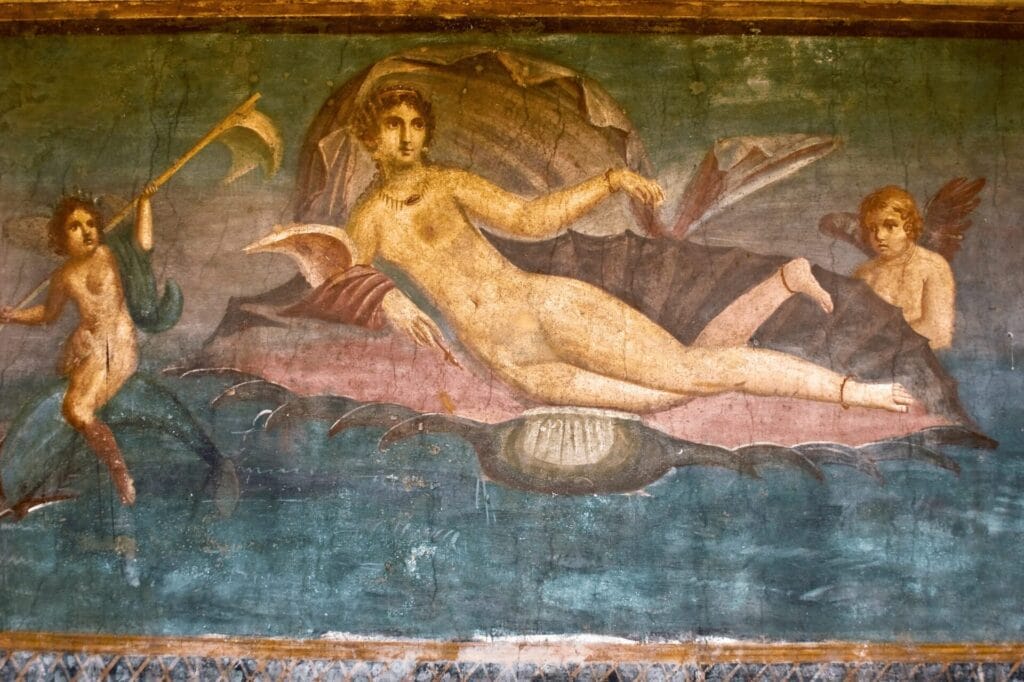

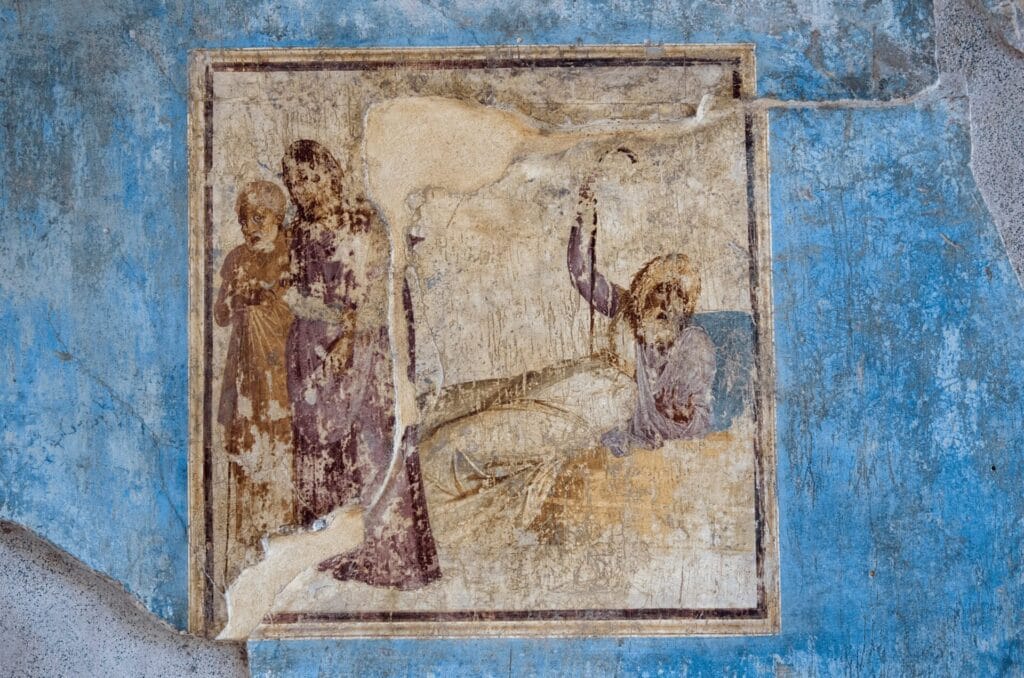
The Rediscovery of Pompeian Art during the Renaissance
The early excavations at Pompeii marked a crucial moment in art history, reshaping our understanding of Roman culture and its artistic practices. Beginning in the 18th century, these archaeological efforts unveiled a treasure trove of frescoes, sculptures, and artifacts that had been buried under volcanic ash for nearly two millennia. The discovery of these remarkably preserved artworks offered an unprecedented glimpse into the life and aesthetics of ancient Rome.
Key Figures in the Rediscovery
Key figures played essential roles in this rediscovery:
- Rocque Joaquin de Alcubierre: Leading the initial excavation efforts, Alcubierre uncovered significant sites within Pompeii. His approach often prioritized finding treasures over meticulous documentation. Despite this limitation, his work laid the groundwork for future studies.
- Karl Jakob Weber: Following Alcubierre, Weber introduced more systematic methodologies. He emphasized careful documentation of artifacts and their contexts, bridging the gap between treasure hunting and scientific archaeology.
These early excavators were driven by curiosity about classical antiquity. They unearthed not just physical remains but also rich insights into Roman life through frescoes depicting domestic scenes, mythological narratives, and public events.
Influence on Renaissance Artists
The influence on Renaissance artists was profound. As these excavations progressed, artists and scholars began to recognize the aesthetic qualities inherent in Roman frescoes:
- Revival of Techniques: Artists such as Raphael and Michelangelo drew inspiration from the vibrant colors and dynamic compositions found in Pompeian art. This revival led to a renewed interest in classical techniques that had largely faded during the Medieval period.
- Emphasis on Naturalism: The detailed depictions of human figures and everyday life in Pompeian frescoes informed Renaissance artists’ approaches to realism. They sought to emulate the lifelike portrayals that characterized Roman artworks.
- Integration into Artistic Education: The rediscovered frescoes became essential study subjects for aspiring artists during the Renaissance. Workshops began to incorporate these works into their curricula, allowing students to learn from authentic examples of ancient artistry.
As more excavation reports circulated throughout Europe, fascination with Roman art grew exponentially. Books featuring illustrations of Pompeian murals spread awareness among artists and intellectuals alike. This dissemination fostered an environment ripe for innovation as Renaissance artists sought to blend classical inspiration with contemporary themes.

Transformation of European Art
The interplay between archaeology and artistry during this period resulted in a remarkable transformation within European art. The incorporation of vibrant colors, intricate details, and classical motifs seen in Renaissance works can be traced back to discoveries made at Pompeii.
In summary, the rediscovery of Pompeian art served as a catalyst for a broader cultural movement that embraced ancient techniques while pushing against traditional boundaries. This dialogue between past and present enriched artistic expression during the Renaissance and continues to inform our appreciation of Roman culture today.

Preserving the Legacy: Techniques and Challenges in Conserving Pompeian Frescoes Today
The preservation of frescoes from Pompeii and Herculaneum is a complex endeavor that combines historical reverence with modern technology. As these ancient artworks are vital windows into Roman life, understanding the methods used to conserve them enhances our appreciation of their cultural significance.
Innovations in Preservation Techniques
Archaeologists have developed several innovative methods to safeguard these delicate frescoes:
1. Plaster Casting
One of the most groundbreaking techniques introduced by Giuseppe Fiorelli in the mid-19th century. This method involves creating molds using plaster to capture the shapes left by organic materials, such as human bodies or furniture, that decomposed over time. The resulting casts provide not only a glimpse into the physical presence of individuals at the moment of catastrophe but also an indirect view into daily life.
2. Microclimate Control
Modern conservation efforts focus on controlling environmental factors such as humidity and temperature. Specialized display cases and climate-controlled environments protect frescoes from moisture damage and temperature fluctuations, which can lead to deterioration.
3. Chemical Treatments
Researchers have explored various chemical solutions to stabilize pigments and binders in frescoes without compromising their integrity. These treatments help maintain color vibrancy while preventing further decay caused by exposure to air pollutants or biological growth.
Ongoing Challenges in Conservation
Despite advancements, challenges remain significant in preserving these irreplaceable artworks:
- Natural Deterioration: The original materials used in fresco painting are susceptible to degradation over time. Factors such as water infiltration, salt crystallization, and general wear can affect both the painted surface and underlying plaster.
- Visitor Impact: The increasing number of tourists visiting Pompeii poses risks to fresco preservation. Foot traffic can introduce dirt, moisture, and other contaminants that may accelerate deterioration. Managing visitor access while allowing for public appreciation remains a delicate balance for conservators.
- Limited Funding: Conservation efforts are often constrained by financial limitations. Securing adequate funding for ongoing research, restoration projects, and preventive measures is essential yet challenging given competing priorities within archaeological sites.

The Importance of Conservation
The work being done today is crucial for ensuring that future generations can appreciate these captivating glimpses into Roman civilization. Each preserved fresco tells a story:
- Idyllic landscapes transport viewers back to ancient Rome’s scenic vistas.
- Religious rites depicted in vibrant colors highlight the spiritual beliefs that shaped daily life.
The techniques developed over centuries reflect an ongoing commitment to maintaining this cultural heritage. Through careful preservation practices, we gain invaluable insights into Roman society’s aesthetics, social structures, and religious customs.
In preserving these murals, you participate in a broader conversation about cultural legacy. Every effort made today reinforces the connection between past civilizations and contemporary understanding. This commitment ensures that frescoes from Pompeii will continue to serve as windows into Roman life for many years to come.

The Enduring Impact of Pompeian Frescoes on Our Understanding of Ancient Rome
Studying the frescoes from Pompeii and Herculaneum reveals much more than mere aesthetics. These vibrant artworks serve as crucial educational tools, offering insights into the complex tapestry of ancient Roman life. The murals depict a wide range of subjects, including:
- Idyllic Landscapes: Scenes that showcase the natural beauty and environment of the time.
- Domestic Life: Intimate depictions of family interactions, daily chores, and social gatherings.
- Religious Rites: Illustrations of rituals and deities that played significant roles in Roman belief systems.
These elements highlight various facets of Roman culture, from social hierarchies to familial connections.
Insights into Social Structures
The frescoes are not just artistic expressions; they are windows into the societal norms and values of ancient Romans. For instance:
- Public Events: Murals depicting banquets and games underscore the importance of community interactions and socialization.
- Domestic Spaces: Scenes within homes demonstrate gender roles and family dynamics, revealing how these relationships shaped everyday life.
Each fresco provides context for understanding how Romans navigated their world, illustrating customs that may seem foreign yet resonate with universal human experiences.

Technical Mastery
The technical aspects of fresco painting also offer invaluable knowledge. The true fresco technique, where pigments are applied to wet plaster, ensures durability while maintaining color vibrancy. This method not only enhances the visual appeal but also reflects the sophistication of Roman artistry.
Renaissance Rediscovery
During the Renaissance, artists revisited these ancient techniques, which significantly influenced contemporary art styles. The revival of classical ideals stemmed from a fascination with Roman aesthetics, showcasing how historical art can inspire future creativity.
Importance of Ongoing Research
Research into these frescoes remains essential today for several reasons:
- Cultural Education: Continual exploration allows us to grasp diverse aspects of Roman civilization.
- Art Historical Relevance: Understanding these works enriches our appreciation for artistic development over time.
- Preservation Efforts: Ongoing studies contribute to better techniques in conserving fragile artworks for future generations.
The enduring legacy of Pompeian frescoes lies in their ability to educate us about a civilization that has profoundly influenced Western culture. Engaging with these artworks fosters a deeper connection to history while emphasizing the importance of preserving such treasures for collective memory. Each mural continues to tell stories that transcend time, inviting you to explore the rich tapestry of Roman life through their vivid expressions.

FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are frescoes from Pompeii and why are they significant?
Frescoes from Pompeii are wall paintings created on wet plaster, which allowed for vibrant colors and dynamic compositions. They are significant as they provide a glimpse into the daily activities, social customs, and religious practices of ancient Romans, offering valuable insights into their vibrant culture.
How did the eruption of Mount Vesuvius impact the preservation of Roman frescoes?
The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 C.E. buried the cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum under ash and pumice, creating an environment that preserved these remarkable frescoes for centuries. This preservation allows modern scholars to study and understand Roman life and art.
What techniques were used by Roman artists in creating frescoes?
Roman artists employed the true fresco technique, which involved applying pigments on wet plaster. This method resulted in vibrant colors and ensured the longevity of the artwork, allowing for dynamic compositions that depicted various themes such as landscapes, mythology, and daily life.
What themes can be found in Pompeian frescoes?
Pompeian frescoes depict a variety of themes including idyllic landscapes, domestic life, public gatherings, entertainment, mythology, and religious rites. These artworks reflect family life, social structures, community interactions, and religious beliefs prevalent in ancient Rome.
How did Renaissance artists influence their work through the rediscovery of Pompeian art?
Renaissance artists were significantly influenced by early excavations at Pompeii. Discoveries made by archaeologists like Rocque Joaquin de Alcubierre helped them rediscover ancient techniques used in fresco painting, which subsequently shaped Renaissance art styles.
What challenges do conservators face when preserving Pompeian frescoes today?
Conservators face ongoing challenges in preserving Pompeian frescoes due to their delicate nature. Modern preservation methods must address issues such as environmental damage and deterioration while ensuring that these artworks can be appreciated by future generations.

