Roman art holds a pivotal place in the annals of history, renowned for its diversity and innovation. This art form not only mirrored the vast expanse of the Roman Empire but also its cultural dynamism. Through the fusion of styles and influences, Roman art offers a window into the complexities of ancient life.
Key mediums in Roman art include mosaics, pottery, and frescoes. Mosaics showcased intricate designs using colored stones and glass, adorning both public and private spaces. Pottery, known for its durability and decorative appeal, captured everyday scenes with finesse. Meanwhile, frescoes, painted onto wet plaster, brought walls to life with vivid depictions of mythology and daily activities. These mediums collectively offer invaluable insights into Roman life, society, and aesthetics.
Mosaics: A Window into Roman Life
Roman mosaics stand as remarkable examples of ancient artistry, crafted from small pieces of materials known as tesserae. These intricate artworks, prevalent across the Roman Empire, adorned both private residences and public buildings, serving decorative and functional roles. Mosaics not only showcased the artistic ingenuity of the Romans but also provided a vivid depiction of daily life.

Common themes depicted in Roman mosaics reflect the essence of everyday Roman society. Scenes of gladiator contests and agricultural activities highlight both leisure and labor. The Romans’ appreciation for the natural world is evident in mosaics featuring flora and fauna. Additionally, detailed portraits capture the personal identities and status of individuals, underscoring the importance placed on societal roles.
Moreover, mosaics often incorporated mythological and sea motifs, illustrating the cultural influences from Greek narratives. Geometric and decorative patterns were popular, especially in Roman baths, reflecting aesthetic preferences and the cultural exchanges within the empire. These mosaics serve as invaluable records, providing insight into the values and daily experiences of ancient Romans.
Pottery: Everyday Scenes Captured
Pottery played an indispensable role in everyday Roman life, serving both practical and aesthetic purposes. As essential containers, pottery housed items like food, drinks, and medicine, catering to a range of needs from mundane to ceremonial. The diversity of pottery, whether fine ware for formal occasions or coarse ware for daily use, highlighted the social stratification within Roman society.

Artistically, Roman pottery was a canvas for illustrating daily life and cultural values. Scenes of symposia—male drinking parties—featured prominently, reflecting the importance of social gatherings. Women were often depicted in the act of water collection, emphasizing domestic responsibilities and societal roles. Additionally, pottery captured the use of oils in grooming and rituals, as small containers like alabastra depicted personal care routines.
Pottery also served ceremonial roles, often used in religious practices and as funeral offerings. These depictions provided insights into Roman cultural practices, bridging the gap between the mundane and the mystical. Through both form and function, Roman pottery remains a vital source of understanding the intricacies of ancient daily life.
Frescoes: Art on Walls
Fresco painting stands as a testament to Roman artistic ingenuity, characterized by its technique of applying water-based pigments on freshly laid wet plaster. This method, known as the Buon Fresco Technique, ensures that colors bond seamlessly with the wall, resulting in vibrant and enduring artworks. Roman frescoes are renowned for their vivid hues and intricate designs that have withstood the ravages of time.

Commonly found in significant archaeological sites like Pompeii and Herculaneum, these frescoes adorned the walls of homes, public buildings, and temples, offering a window into various facets of Roman life. The themes depicted in these frescoes are diverse, ranging from mythological narratives to scenes of everyday life. Domestic frescoes often portrayed intimate family moments and household activities, while public frescoes reflected civic pride and the grandeur of urban life.
Such depictions not only served as decorative elements but also provided insights into the cultural and social dynamics of ancient Rome. By exploring these artistic masterpieces, we gain a deeper understanding of Roman society and its lasting influence on the art world.
Social Hierarchies in Art
Roman art serves as a visual narrative of the complex social hierarchies that defined ancient Roman society. Through various mediums such as mosaics, frescoes, and pottery, artists depicted the distinct roles and statuses of different social classes. For instance, elaborate frescoes found in affluent Roman villas often portrayed the opulent lifestyles of the elite, featuring scenes of banquets and leisure activities, underscoring their wealth and influence.
Conversely, pottery and simpler mosaics frequently depicted the everyday lives of the lower classes, including laborers and farmers. These artworks highlighted their contributions to Roman society, such as agricultural work and craftsmanship, illustrating the foundational roles they played in the economy. Art, therefore, not only celebrated the grandeur of the upper echelons but also acknowledged the essential functions of common citizens.
This artistic representation of class distinctions offers valuable insights into the social structures of the time, reflecting both the disparities and interdependencies within Roman civilization. The ability of Roman art to encapsulate these societal dynamics continues to inform our understanding of ancient cultural and social life.
Banquets and Feasts
In the social fabric of ancient Rome, banquets held significant cultural importance. These gatherings were more than mere meals; they were a reflection of Roman society’s intricate hierarchies and social networks. Banquets served as platforms for displaying wealth and status, forging alliances, and showcasing cultural sophistication. They were often grand affairs, complete with lavish foods, elaborate settings, and entertainment, embodying the opulence of the Roman elite.
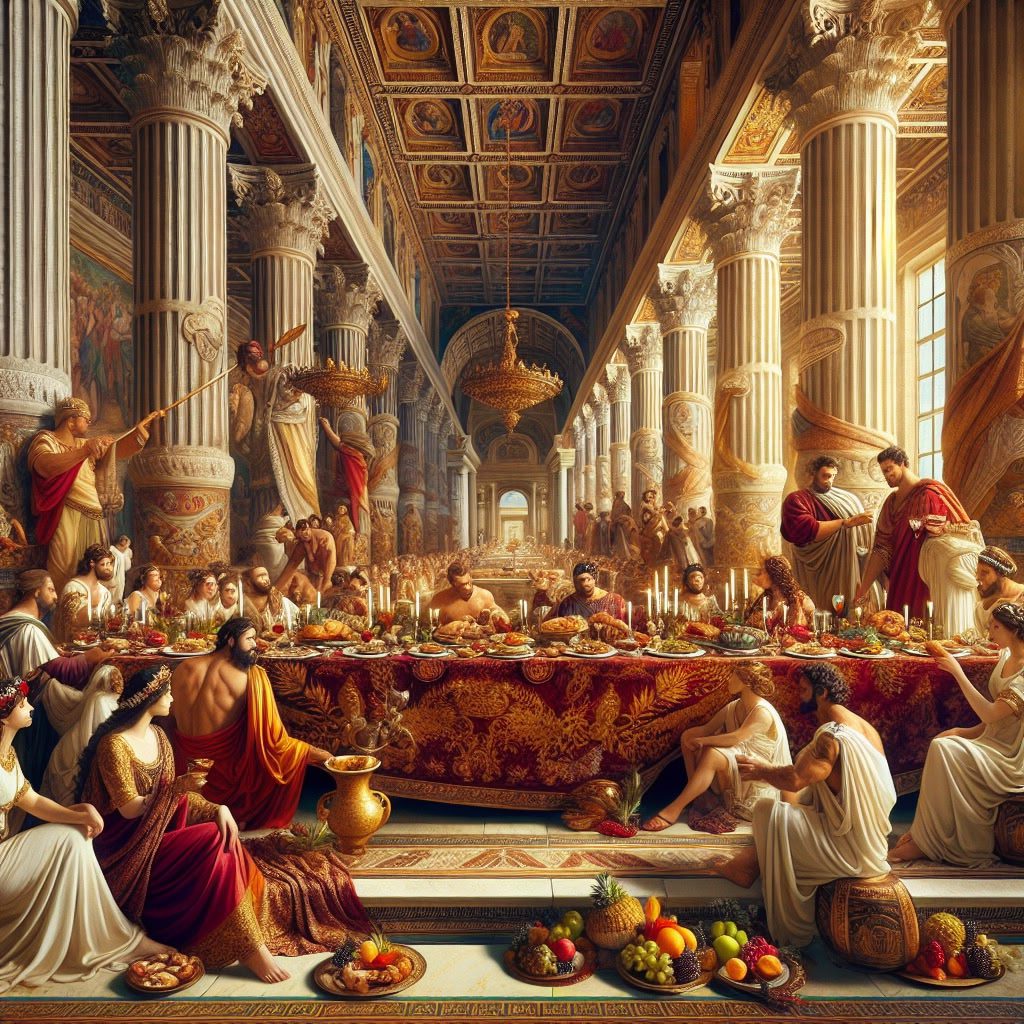

Artistic depictions of feasting scenes in Roman art provide a window into the societal norms and values of the time. Mosaics and frescoes frequently illustrated these banqueting scenes, capturing the elegance and grandeur of the occasion. Such artworks depicted diners reclining on couches, surrounded by servants, musicians, and dancers. The meticulous detailing in these artworks highlighted the importance of hospitality and the role of banquets as a social institution. This visual documentation not only celebrated the affluence and leisure of the upper classes but also offered insights into the daily life and customs of ancient Rome. Through these artistic expressions, modern viewers can appreciate the social dynamics and cultural richness of Roman civilization.
Leisure and Entertainment
Roman art vividly captures the essence of leisure and entertainment, reflecting the diverse pursuits that characterized ancient Roman society. Common leisure activities depicted in art include chariot races, gladiatorial games, theatrical performances, and public baths. These pastimes were integral to Roman culture, offering avenues for relaxation and communal engagement.

Chariot races and gladiatorial games were not merely pastimes but grand spectacles that drew citizens together, transcending social classes. These events, often held in colossal arenas like the Colosseum, served as focal points of public life, fostering a sense of unity and shared excitement among the populace. Theatrical performances, depicted in frescoes and mosaics, highlighted the Romans’ appreciation for drama and storytelling, enriching their cultural landscape.
The role of entertainment in Roman society was multifaceted, acting as a medium for social interaction, cultural expression, and political communication. Artworks portraying these activities not only illustrate the vibrancy of Roman life but also underscore the importance of entertainment as a societal glue that bound communities together, providing insights into the values and priorities of ancient Rome.
Agricultural Scenes
Agriculture was a cornerstone of the Roman economy, sustaining not only the empire’s vast population but also its military and urban centers. The fertile lands of the Roman territories provided essential crops such as wheat, olives, and grapes, which were pivotal for trade and sustenance. This agricultural abundance was crucial in maintaining Rome’s economic stability and expansion.

In Roman art, the significance of agriculture is well-documented through various mediums, including frescoes and mosaics. These artworks often depicted bucolic landscapes, laborers in fields, and scenes of harvest, highlighting the integral role of farming in daily life. For instance, frescoes from sites like Pompeii illustrate farmers at work, showcasing the tools and techniques employed in agriculture.
Such depictions offer valuable insights into the agricultural practices of ancient Rome, reflecting the society’s reliance on farming and its celebration of rural life. By capturing these scenes, Roman artists not only immortalized the agricultural processes but also emphasized their cultural and economic importance in sustaining the empire’s prosperity.
Influence on Later Art Movements
The depiction of everyday life in Roman art had a profound impact on artistic movements, most notably during the Renaissance. This era, signifying a “rebirth,” saw a revival of ancient Roman culture, where artifacts became crucial sources of inspiration for artists seeking to emulate classical achievements. Roman art’s emphasis on realism and naturalism, evident in its portrayal of human figures and daily scenes, inspired Renaissance artists to explore new techniques and perspectives.

Renaissance artists like Nicola di Maestro Antonio drew heavily from Roman precedents, employing perspective and color selection to achieve realistic representations. This laid the foundation for realism, which would later influence artists such as Gustave Courbet, who portrayed life with gritty authenticity. Roman art’s legacy of depicting natural-looking figures, often dramatic and emotional, fueled artistic innovation well into the modern era, showcasing its enduring influence on art’s evolution.
Ultimately, the realistic portrayal of everyday life in Roman art not only enriched the Renaissance but also set a precedent for future movements, encouraging artists to capture the essence of human experience with depth and authenticity.
Data and Statistics
The analysis of surviving Roman artworks offers valuable insights into the diverse themes and subjects depicted in this ancient art form. Roman art, influenced by Greek, Egyptian, and Etruscan cultures, spans nearly a millennium and reflects a vast array of styles and media. A significant portion of surviving artworks includes marble statues, often Roman copies of Greek originals, underscoring the tradition of replication.

To better understand these trends, consider the following table:
| Art Form | Common Themes | Surviving Artworks |
|---|---|---|
| Mosaics | Daily Life, Mythology | 500+ |
| Pottery | Household Scenes | 300+ |
| Sculpture | Portraiture, Historical Events | 1,000+ |
| Frescoes | Domestic Life, Nature | 200+ |
The statistical trends indicate a strong emphasis on realism and individualism, particularly in portraiture and funerary art. Themes of daily life and mythology were prevalent in mosaics and frescoes. Moreover, the accessibility of art grew, allowing for personal enjoyment across social classes, which is evident in the diversity of themes and subjects depicted.
Key Takeaways
Roman art provides profound insights into the daily lives and cultural values of the Roman civilization. By examining art forms such as mosaics, pottery, and frescoes, we can unravel the complexities of Roman society.

- Diverse Influences: Roman art was heavily influenced by Greek, Egyptian, and Etruscan cultures, as reflected in the replication of Greek statues and the incorporation of various artistic traditions.
- Realism and Individualism: Roman artists prioritized lifelike portrayals and individual characteristics, which is evident in portrait busts and funerary art.
- Depictions of Daily Life: Artworks frequently captured everyday scenes, from banquets to agricultural activities, offering a glimpse into the lives of different social classes.
- Historical and Cultural Documentation: Roman art documented historical events and cultural narratives, preserving the empire’s legacy through triumphal arches and mythological scenes.
The significance of Roman art extends beyond its aesthetic value. It serves as a crucial historical record that aids our understanding of social structures, cultural exchanges, and the evolution of artistic practices over time. The legacy of Roman art, influencing movements like the Renaissance, underscores its lasting impact on the art world.

Conclusion
Roman art, spanning nearly a millennium, provides an invaluable lens into the daily lives and cultural nuances of the Roman Empire. From intricate mosaics depicting vibrant social scenes to pottery illustrating everyday activities, these artworks offer a rich tapestry of Roman life. The realism and individualism captured in these pieces underscore the Romans’ devotion to lifelike representation and cultural documentation.
The historical importance of Roman art lies not only in its aesthetic achievements but also in its ability to bridge the past with the present, influencing movements like the Renaissance. As we reflect on its enduring legacy, Roman art remains a testament to a civilization’s dedication to creativity, cultural exchange, and historical preservation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What influenced the styles and themes in Roman art? Roman art was heavily influenced by the cultures within its empire, especially Greek, Egyptian, and Etruscan. This blend led to a diverse artistic tradition characterized by eclecticism and realism.
Why are there so many Roman copies of Greek statues? Many surviving marble statues are Roman copies of Greek originals. Romans admired Greek art and often replicated it as a way to preserve and honor those artistic traditions, which is highlighted in the replication practices of Roman artists.
What themes were commonly depicted in Roman art? Roman art featured a variety of themes, including mythology, daily life, and historical events. These themes were often portrayed in mosaics, frescoes, and sculptures, reflecting both grandeur and everyday activities.
How did Roman art influence later artistic movements? Roman art significantly influenced the Renaissance and later movements by preserving and propagating key artistic traditions, such as realism and attention to detail, which were highly valued in subsequent art periods.

